problem 1) Categorical variable tread Pattern = {A, B} and numerical variable tread Depth are used to classify Handling = {good, poor} of a vehicle. Depth is normally distributed with mean 9 and standard deviation 3 when Handling is good and mean 16 and standard deviation 4 when Handling is poor.
There are 300 rows of data for training and the number of rows of data for each combination of Pattern and Handling are given in the table below.
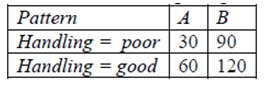
Given row x0 = (Pattern = A, Depth=12). Use a naive Bayes’ classifier to compute the class of Handling assigned to x0. Show your work for full credit.
problem 2) Consider the following neural network for two predictors Thickness and Alignment and two classes Print Quality High and Low. Some weights are shown in the table, including weights for constant (threshold) nodes that link to each output node.
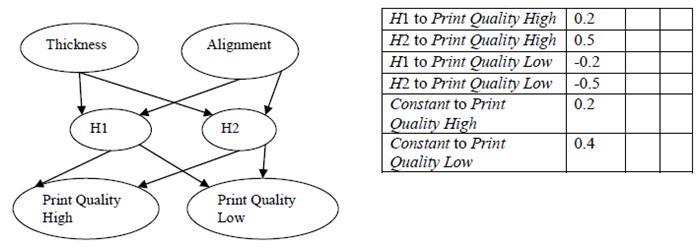
Suppose input data row x0 produces z1 = 0.5 at node H1 and z2 = 0.4 at node H2. Assume the softmax function is used at the outputs. Compute the output at each output node. To what Print Quality class is row x0 assigned?
problem 3) In either the design or training of a neural network, provide a list of several ways to reduce the complexity of the model.
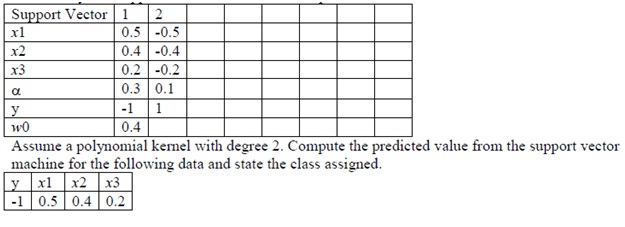
problem 4) Consider a support vector machine with three inputs x1, x2, and x3. Assume there are only two support vectors with values and parameters as follows:
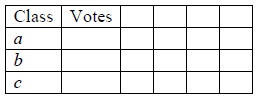
problem 5) Consider one versus the rest voting used for classifier with three classes {a, b, c}. Given a row of data denoted as x0 suppose that the classifier for a versus the rest predicts the rest, b versus the rest predicts the rest, and c versus the rest predicts c. What are the votes for each class for x0?
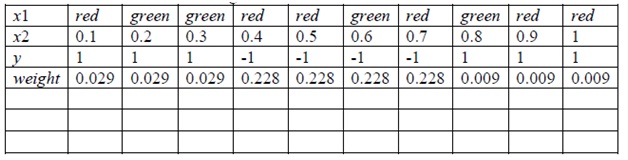
problem 6) Consider the data with categorical predictor x1 = {green or red} and numerical predictor x2 and the class variable y shown in the following table. The weights for a round of boosting are also shown in the table. Suppose the classifier built from this round of boosting assigns y = 1 for x2 < 0.45 and y = -1 for x2 > 0.45. Compute the coefficient α for this classifier in the boost algorithm.
problem 7) A data set with 1000 rows is input to a neural network in Weka. The test option is set to 10-fold cross validation and the neural network option validationSetSize = 20%. How many rows of data are used in a validation set in a fold?
A support vector machine in Weka uses a Gaussian (radial basis function) kernel with parameter gamma. Gamma should be selected less than or equal to one. Circle True or False.
A support vector machine in Weka uses a Gaussian (radial basis function) kernel with parameter gamma = 0.2. This corresponds to the parameter σ2 equal to what value?
problem 8) Given a dataset with 1000 rows and 25 predictors labeled x1, x2, …,x25 to classify into two classes {a, b}. Consider the small random forest with 3 trees and one split in each tree as shown below. Here 5 predictors are selected randomly at each node. The class assigned to each leaf node is also shown.
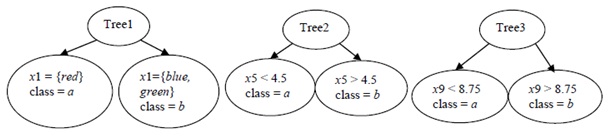
a) Given a row of data x0 with x1= green, x5 = 4, x9 = 9, predict the class label for the row.
b) For Tree1, it can be concluded that the best split among all 25 predictors is obtained from x1. Circle True or False.
c) Approximately 368 rows are expected to be out of bag for Tree 1. Circle True or False.
d) Categorical variables are coded to {0, 1} indicator variables in a random forest. Circle True or False.
problem 9) Suppose the random sample used for each tree in the previous random forest is decreased from 1000 rows to 500 rows. Circle ALL that are true for the ensemble classifier.
a) Variance of predictions is expected to decrease.
b) Bias of predictions is expected to decrease.
c) Each base classifier is expected to have more out of bag rows of data.
d) Generalization error is expected to decrease.
problem 10) A Bayesian network is shown for the variables paper Thickness, paper Alignment and Print Quality. The conditional probabilities are provided in the tables beside the nodes. Here, Thickness = {high or low}, Alignment = {straight or angled}, and Print Quality = {good or bad}.
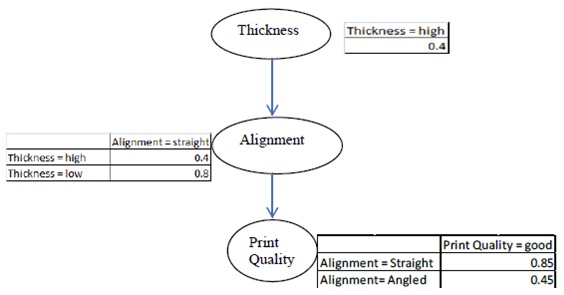
find out the following quantities from the information in the Bayesian network.
a) P(Alignment = straight)
b) P(Alignment = straight | Print Quality = good)