Robot Position Calculation
1. Program Overview and Theory
Overview
The Pololu robot has a mechanical encoder attached to each wheel. Each encoder produces 45 electronic pulses for each revolution of the wheel. The program will use the wheel pulse counts to calculate the position and heading (direction) of the robot.
The program is a C++ program that runs on the Pololu robot. The program gets the wheel pulse counts on the robot and calculates the resulting robot position and heading. Each calculated position is transmitted by the Wixel wireless module to the PC, to be displayed on the PC screen.
Program Calculations
Use the following formulas to calculate the change in robot position and then the new position, based on the physical dimensions of the robot and the number of pulses from each wheel since the previous position calculation.
robot constants
a = robot axle length = 5.0 cm
w = robot wheel diameter = 3.6 cm
p = pulses per wheel revolution = 45
d = distance a wheel travels for each wheel pulse = Π.w/p cm
robot position and heading variables
X = robot x coordinate
Y = robot y coordinate
H = robot heading (direction, measured anticlockwise from the positive x axis)
number of pulses (since the previous calculation)
L = number of pulses from the left wheel
R = number of pulses from the right wheel
position calculations if L equals R:
δH = change in robot heading = 0
δX = change in robot x coordinate = L.d.cos(H)
δY = change in robot y coordinate = L.d.sin(H)
if L is not equal to R:
r = radius of curvature of the robot trajectory = ½.a.(R+L)/(R-L)
δH = change in heading = (R-L).d/a
δX = change in x coordinate = r.(sin(H+δH) - sin(H))
δY = change in y coordinate = r.(cos(H) - cos(H+δH))
[Be especially careful to write the formula for δY correctly!]
Then calculate the new values of H, X and Y as follows:
H = H+δH
X = X+δX
Y = Y+δY
Suggestion: In your program use the variable names dH, dX and dY for δH, δX, and δY.
The above formulas assume the wheels are running forward. If a wheel is running backwards (in reverse) then the above formulas are also correct, if the number of pulses from a reversing wheel is converted to a negative value.
Mathematics Theory
The appendix to this document "Derivation of the Robot Position Formulas" shows the derivation of the formulas for the change in robot position and heading. The derivation is given for information only. You are only required to use the resulting formulas in your program. However, this derivation shows a typical use of mathematics in engineering.
2. Program Specification
Overview
Write a program for the Pololu robot using the mbed compiler, where:
- the robot moves, with each wheel running at its own constant speed,
- the wheel speeds can be any number between 0.0 and 1.0, inclusive,
- the wheel speeds will be constants in the program, so to change the speeds, the program must be modified and recompiled,
- use a time delay to get the wheel pulse counts every 10-100 ms (depending on the wheel motor speed),
- functions are provided to get the wheel pulse counts when required,
- the robot position is calculated using appropriate formulas (as given),
- the position is transmitted to the PC using the Wixel wireless module (where the position is displayed and the robot trajectory is plotted using the PololuPositionDisplay program provided on Blackboard).
Program Details (Pseudocode)
Once only, at the start, the program should:
- display the program title on the robot LCD,
- set the Wixel speed (baud rate) to 115200,
- display the program title on the PC,
- display the battery voltage, wheel speeds and loop time delay on the PC,
- initialise the robot coordinates X, Y and heading H to zero,
- display suitable headings for the columns of numbers,
- display the initial values of X, Y and H on the PC,
- call the provided function to initialise the encoders,
- turn the motors on using the speed constants.
Then inside the while(1) loop, the program should repeatedly:
- wait for 10-100ms (depending on the wheel speed) using the mbed wait_ms function,
- get the number of pulses from each encoder (L, R) using the given functions,
- display the pulse counts L, R on the LCD display,
- if either pulse count is not zero, calculate the change in robot position dX, dY, dH (using the given formulas),
- calculate the new robot position X, Y, H (using the given formulas),
- display the new robot position X, Y, H and the pulse counts L, R on the PC.
Program Code
The file Assignment.cpp on Blackboard contains program code you can use. You need to:
- add code where there are blank lines,
- add conditions to the two if statements.
The source files encoder.cpp and encoder.h are provided on Blackboard. You need to copy and paste this code into mbed files, with the same names, in your program on the mbed website.
These files contain functions to operate the robot encoders.
Hints
Remember the trig functions need angles in radians, so use H in radians in your program, but display the angles in degrees, not radians.
The given cpp file contains the definition for Π because Π is not defined in the mbed math libraries.
Once the robot starts moving, the while (1) loop ensures the robot keeps moving until the robot power is turned off.
When sending the robot position to the PC, the string for each line must start with "POS," and the numbers must be separated by commas. This ensures the PC program recognises the lines of text that are the robot position, so the plot can be drawn correctly. Extra spaces are allowed.
3. Sample Program Settings and Output
The following example shows typical output transmitted from the robot to the PC. Your program should produce similar output, but your output will not be exactly the same due to differences between the robots. The PololuPositionDisplay application program is available on Blackboard as part of this assignment
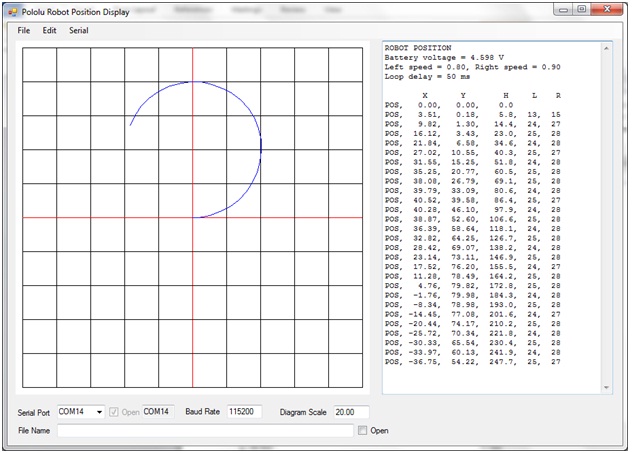
The wait period between position calculations was set to 50ms. However, the calculations and data transmission to the PC take about 10ms in addition to this, so the position calculations are approximately 60ms apart.
The left wheel speed was 0.8 and the right wheel speed was 0.9.
From the scale, the robot trajectory circle diameter is about 80cm, so it is possible to run this program with the robot on the floor, when there is this much clear space.
If the wheel speeds are set to the same value, the robot travels in a much larger circle with a diameter up to 10 m, which is too big for the confined space available on the floor in the lab or the nearby corridor. The trajectory is also much less circular because small changes in the actual wheel speeds cause significant variations in the trajectory.
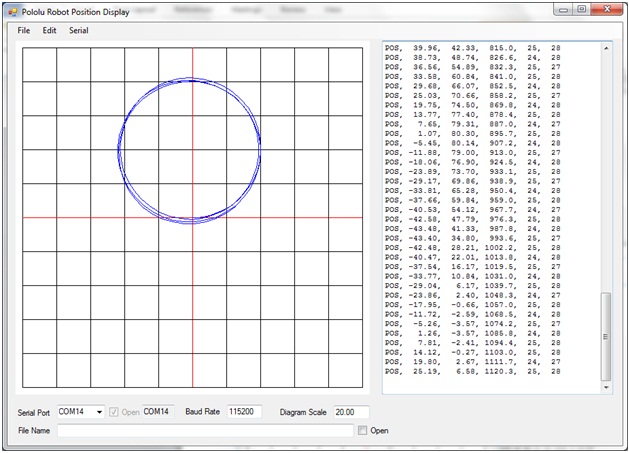
The plot on the next page used the same robot, with the same speed and time delay settings as used above. This plot shows the end of the run (when the robot was stopped).
Notice that the robot heading steadily increases, because the heading increases by 360 degrees for each circle of the trajectory. At the end of the run, the heading is 1120.3 degrees because the robot has just completed its third circle.
4. Assessment
The assessment of your program for this assignment will be based mainly on (but may not be limited to) the following points:
- Source code compiles and links ("builds") without any errors or (significant) warnings.
- Source code is correctly formatted (correct layout).
- Uses appropriate named constants.
- Uses appropriate variable names.
- Displays a program title on the LCD and PC.
- Displays the battery voltage on the PC.
- Displays the motor speeds and loop time delay on the PC.
- Displays column headings on the PC.
- Displays pulse counts on the LCD.
- The calculations are correct.
- On the PC, the displayed robot position and pulse counts are well formatted.
- The robot trajectory is displayed on the PC.
The program will be tested using various wheel speeds, including equal wheel speeds and different wheel speeds.
Attachment:- Appendix.rar