Consider the space for a maze as being a large grid of cells with each cell holding four 'walls'. Starting with a random cell, the computer randomly chooses a neighboring cell. The computer removes the walls between two cells and adds the initially, randomly chosen cell to a stack. Once a cell has at least one wall removed, it is considered to have been visited. The computer continues this procedure. Any cell that has no unvisited neighbors’ is considered a dead-end. When at a dead-end the computer backtracks through the path by popping the stack till it reaches a cell with at least one unvisited neighbor, and continues the path generation by visiting this new, unvisited cell. This process continues till every cell has been visited. This depth-first search approach is captured in the subsequent algorithm:
1. Randomly choose an initial cell
2. While there are neighboring cells with all four walls intact
i. Randomly select one of the unvisited neighbors’
ii. Push the selected cell to the stack
iii. Remove the wall between the current cell and the chosen cell
3. Pop a cell from the stack and make it the current cell
4. Repeat from step 2 until all cells have been visited
Follow the instructions below to prepare the program that will create a representation of a maze by using the depth-first search algorithm.
1. Make the following ADTs.
(a) prepare constructor function makestk, predicate function emptystk and mutator functions pushstk and popstk:
i. makestk returns a new stack in form of a tagged tuple: ('stack',[]).
e.g. >>> cellstk=makestk()
>>> cellstk
('stack', [])
ii. emptystk returns True or False depending on whether the given stack is empty or not.
e.g. >>> emptystk(cellstk)
True
iii. pushstk accept a stack and an element, and adds the element to the stack at position 0 (see part (b) below for the creation of cell0).
e.g. >>> pushstk(cellstk,cell0)
>>> cellstk
('stack', [('cell', (0, 0), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l'])])
iv. popstk eradicates the element at position 0 of the given stack.
e.g. >>> popstk(cellstk)
('cell', (0, 0), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l'])
>>> cellstk
('stack', [])
(b) prepare a constructor function called makecell, accessor functions getx, gety and getwalls, and mutator functions removetw, removebw, removerw, removelw.
i. make cell accept a tuple which consists of the x and y co-ordinate of the cell being created. It returns a cell in the form of a tagged tuple:
('cell',(x,y),['t','b','r','l']).
The list represents the four walls of the cell: top, bottom, left and right.
e.g. >>> cell0=makecell((0,0))
>>> cell0
('cell', (0, 0), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l'])
ii. getx and gety return the x and y co-ordinates (correspondingly) of a given cell.
e.g. >>> getx(cell0)
0
iii. getwalls returns the list of walls that are intact for the given cell
e.g. >>> getwalls(cell0)
['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']
iv. remove removes the associated wall from the list of walls of a given cell.
e.g. >>> removetw(cell0)
>>> cell0
('cell', (0, 0), ['b', 'r', 'l'])
2. prepare the function makegrid. This function accepts a width and height and creates a grid/matrix of cells. The width gives the number of columns and the height the number of rows of the grid that must be created.
e.g. >>> makegrid(4,5)
[('cell', (0, 0), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (0, 1),
['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (0, 2), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']),
('cell', (0, 3), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (0, 4), ['t',
'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (1, 0),['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']),
('cell', (1, 1), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (1, 2), ['t',
'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell',(1, 3), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']),
('cell', (1, 4), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (2, 0), ['t',
'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (2, 1), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']),
('cell', (2, 2), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (2, 3), ['t',
'b','r', 'l']), ('cell', (2, 4), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']),
('cell', (3, 0), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (3, 1),['t',
'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (3, 2), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']),
('cell', (3, 3), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell',(3, 4), ['t',
'b', 'r', 'l'])]
3. Given a cell, we should discover its neighbouring cells i.e. those with which it shares a wall. In the diagram given below, the cells with an x are the neighbours of the cell c. prepare the function getneighbours that admitted a cell, the width and height of the grid, and returns all
neighbours of the given cell.
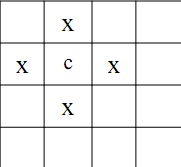
e.g. >>> getneighbours(cell0,4,5)
[('cell', (0, 1), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (1, 0),
['t', 'b', 'r', 'l'])]
4. We must also be capable to remove common walls between two cells. prepare the function removewalls that accepts two cells and removes the wall that is common between the two (hint: any cell will have at most, one wall in common with another).
e.g. >>> cell1=makecell((0,1))
>>> removewalls(cell0,cell1)
>>> cell0
('cell', (0, 0), ['t', 'r', 'l'])
>>> cell1
('cell', (0, 1), ['b', 'r', 'l'])
5. We also want to know, given a cell, which of its neighbours has all of its walls intact. prepare the function wallsintact that accepts the grid and a list of neighbouring cells and returns those whose four walls are integral.
e.g. >>> intact=wallsintact(grid,neighbours)
>>> intact
[('cell', (2, 3), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell',
(3, 2), ['t', 'b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (3, 4),
['t', 'b', 'r', 'l'])]
6. Lastly, prepare function createmaze which accepts a width and height as the dimension for a maze and returns the maze represented as a list of cells. Use depth-first algorithm,
ADTs and functions you created in steps 1-5 above (Hint: Keep track of number of cells visited)
e.g.
>>> createmaze(4,5)
[('cell', (0, 0), ['t', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (0, 1), ['b', 'l']), ('cell',
(0, 2), ['t', 'l']), ('cell', (0, 3), ['r', 'l']), ('cell', (0, 4), ['b',
'l']), ('cell', (1, 0), ['t', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (1, 1), []), ('cell',
(1, 2), ['r']), ('cell', (1, 3), ['b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (1, 4), ['t',
'b']), ('cell', (2, 0), ['t', 'l']), ('cell', (2, 1), []), ('cell', (2,
2), ['b', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (2, 3), ['t', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (2, 4),
['b']), ('cell', (3, 0), ['t', 'b', 'r']), ('cell', (3, 1), ['t', 'b',
'r']), ('cell', (3, 2), ['t', 'r', 'l']), ('cell', (3, 3), ['r', 'l']),
('cell', (3, 4), ['b', 'r'])]
Represents maze and correct path(S=start, E=end):