Assignment 1:
Section
INVESTIGATION - CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM
In the following investigation you will verify the law of conservation of momentum. Set up
Two air pucks ride on a cushion of air, without friction, in the direction of the arrows. They collide against each other. The following diagram was drawn from a photograph taken with a stroboscopic light to show the positions of the two pucks at regular intervals.
The distances on the horizontal and vertical axes on the graph below are in metres. Compare to the actual measurements you determine with your ruler to calculate the scale factor.
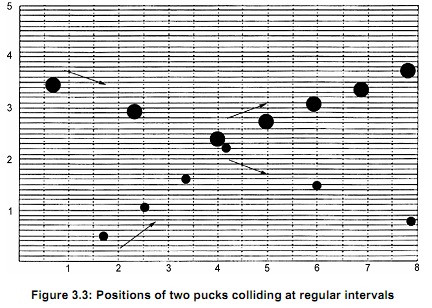
Data:
Mass of the larger puck: 5.4 kg Mass of the smaller puck: 3.6 kg
Period of the strobe light: 1/15 s
Each unit on the graph represents 1.0 m. Procedures:
1. Measure the magnitude of the velocity of each puck and its angle with the horizontal:
a. Measure the distance travelled in one interval of time and divide it by the time.
b. By finding the horizontal and vertical components of displacement between two positions, determine the angles using trigonometry.
2. Calculate the momentum of each of the pucks before collision (remember that momentum is a vector with a direction).
3. Calculate the total momentum of the system before collision by adding the two momenta. Remember to add them as vectors. The total momentum has a magnitude as well as a direction.
To find the magnitude you can use either of the following methods:
a. Adding horizontal and vertical components.
b. Using the sine and/or cosine laws.
4. Measure the magnitude of the velocity of each puck and its angle with the horizontal after collision:
- Measure the distance travelled in one interval of time and divide it by the time.
- By finding the horizontal and vertical components of displacement between two positions, determine the angles using trigonometry.
5. Calculate the momentum of each of the pucks after collision: (remember that momentum is a vector with a direction).
6. Calculate the total momentum of the system after collision by adding the two momenta. Add them as vectors. The total momentum has a magnitude as well as a direction.
7. a. Compare the magnitudes of the total momentum before
collision and the total momentum after collision. Calculate the percentage difference between the two.
b. Compare the angles between the total momentum before and after the collision. What is the difference between the two (in degrees).
8. Enumerate the possible sources of error in this experiment.
9. Draw a conclusion.
Assignment 2:
INVESTIGATION-STATIC EQUILIBRIUM
The following figure shows a beam on which several forces are acting at different points. The beam is in equilibrium. This means that the sum of all the forces acting on it is equal to zero. Since the beam is also in rotational equilibrium, the sum of all the torques around any point of the beam (A in particular) is also equal to zero. You are going to verify these two assumptions using the setting and data provided.
Note
Because of the importance of this investigation with respect to the rest of Part C, it will count for a greater percentage of the marks.
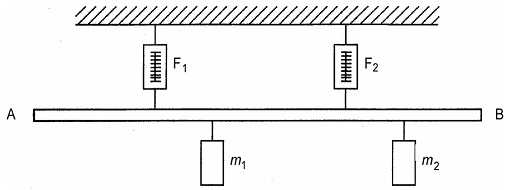
Figure 3.4 A beam in equilibrium
The mass of the beam is 6.00 kg and its length AB = 2.00 m.
|
Force (N)
|
Mass (kg)
|
Distance from A (m)
|
|
F1 = 68.2
|
|
0.45
|
|
F2 = 56.3
|
|
1.71
|
|
|
m 1 = 4.4
|
0.66
|
|
|
mz= 2.0
|
1.84
|
1. Sketch the beam with all the forces acting on it. Hint: Do not forget the mass of the beam itself.
2. Calculate the value of all the forces exerted on the beam.
3. On your sketch, record the distances from each force to the extremity A of the beam.
4. Calculate ∑Fx
5. Calculate ∑Fy
6. Calculate ∑T A
7. Calculate the percentage error found for:
a. ∑Fy
b. ∑TA
8. Draw a conclusion.
Assignment -INVESTIGATION-PROJECTILE MOTION
- A 15-cm or 30-cm ruler graduated in millimetres
- A well-sharpened pencil
- Graph paper (4 sheets)
The following illustration, Figure 1.1, simulates a stroboscopic photograph of two balls falling. One is dropped; simultaneously, the other is projected horizontally.
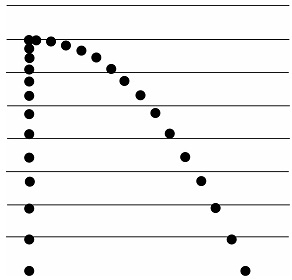
Figure 1.1: Simulation of a stroboscopic photograph of two balls falling; one ball is dropped while the other is simultaneously projected horizontally.
The frequency of the stroboscope used to take the photograph from which the figure is made is f = 30 Hz.
The real distance between two horizontal lines is 14.35 cm.
Procedure:
1. Number the successive positions of each ball.
2. The horizontal line through the first position of the ball on the right will serve as a horizontal base line.
3. Draw a vertical line through the first position of the balls to serve as a vertical base line.
4. Use a ruler to draw lines from each position of the second ball perpendicular to the horizontal baseline.
5. For each flash, measure the horizontal displacement (dx) and the vertical displacement (dy) from the base lines.
6. Measure the length between two successive horizontal lines and calculate the scale factor of the figure. For example, if 1.54 cm of the photograph correspond to 14.35 cm in reality.
You will have to multiply all your displacement measurements by this factor in order to obtain their real length.
7. Calculate the average vertical velocity of the balls between each two flashes. This is done by dividing the real displacement between each two flashes by the time between the flashes (1/30 s). Note that this velocity corresponds to the instantaneous velocity, vy, exactly halfway between two flashes.
8. Calculate the instantaneous horizontal velocity, vx, of the ball on the right halfway between two flashes: Calculate it as the average horizontal velocity between the same two flashes.
9. Make two tables based on the following models, and fill in the appropriate measurements and calculations for all intervals.
10. Graph the following:
dx - time
dy - time
vx - time
vy - time
11. Find the mathematical equation for each of your linear graphs (use slope-intercept).