Purpose
The aim of this experiment is to develop a bipolar transistor amplifier with a voltage gain of minus 25. The amplifier must accept input signals from a source impedance of 1 kW and provide an undistorted output amplitude of 5 V when driving a 560 W load. The bandwidth should extend from below 100 Hz to above 1 MHz.
Problems
1. Calculate the quiescent voltages VB, VE, and VC, and the currents IE and IC for the common emitter circuit in Figure 1. How much power is dissipated in the transistor itself? Is the power safely below Pmax?
2. Find the ac voltage gain of the circuit in Figure 1 for 10 kHz sine waves with the emitter bypass capacitor CE removed. Estimate the maximum amplitude of the output before clipping occurs. (The maximum output voltage is limited by the positive supply voltage, and the minimum is determined by the requirement that the collector voltage must be at least a few tenths of a volt above the emitter voltage.)
3. The emitter bypass capacitor can provide an AC ground path for the emitter, increasing the gain of the amplifier at high frequency. Considering the effects of the intrinsic emitter resistance re, what is the maximum possible AC voltage gain of the amplifier in Figure 1?
Will this gain likely be realized for 10 kHz sine waves? Why or why not?
4. What setting of the emitter trimpot is needed to give the required gain of -25? For the single stage in Figure 1, what are the input and output impedances rin and rout at 10 kHz and a gain of -25? (Note that rin is the impedance looking into the base in parallel with the base divider impedance.) Calculate the fraction of the original amplitude obtained when a 560 W load is connected to the output via a coupling capacitor.
5. Calculate the output impedance for the emitter follower circuit shown in Figure 2. What fraction of the original output amplitude do you expect to obtain when you attach the 560 W load to the emitter follower output?
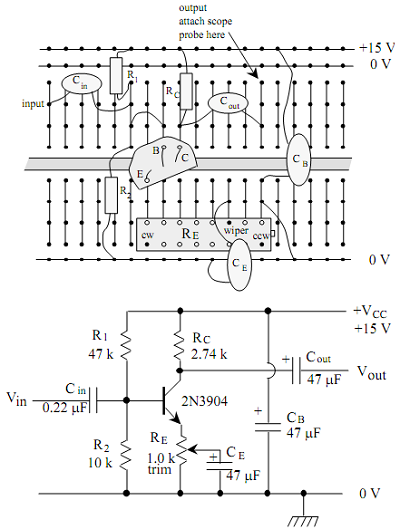
Figure1: Common Emitter Stage Layout and Schematic
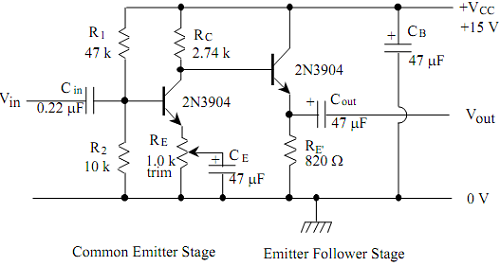
Figure 2: Complete Two-stage Amplifier Circuit
Outline of the Experiment
1 Verify that the 2N3904 is an NPN transistor using the digital multimeter. Is the 2N3906 a PNP or an NPN transistor?
2. Construct a common emitter transistor bias circuit. Confirm that the quiescent voltages are correct. Add coupling capacitors to the circuit to make an ac amplifier, and measure the ac voltage gain for 10 kHz sine waves. Verify that the gain has the expected value, and confirm that the output amplitude can reach 5 V before the extremes of the sine waves are clipped.
3. Make a variable gain amplifier by bypassing part of the emitter resistance with a capacitor. Find the maximum possible voltage gain and compare with your prediction.
4. Adjust the gain to the required value of -25. Find the effect on the output amplitude of placing a source impedance of 1 kW in series with the signal source. Also observe what happens when you place a 560 W load between the output and ground.
5. Now build an emitter follower stage as an impedance buffer between the amplifier and the load. Verify that the emitter follower alone has unit voltage gain. What happens now when you connect the load to the emitter follower output?
6. Test the performance of the complete circuit under the specified conditions: 1 kW source impedance and 560 W load. First reset the overall gain to -25 if it has changed. Check that the 5 V undistorted output amplitude is still available. Measure the gain versus frequency from 1 Hz to 10 Mhz.