Problem 1: (Digital Communications Systems)
digital Communications uses a few specific modulation formats. Research at least 5 different applications or standards and explain what modulation format is used. For example:
"High-capacity terrestrial microwave systems use double-sideband quadrature modula¬tion, the extension of QPSK, with (up to) 1024 signal points and Nyquist filtering, etc " (you may want to add a reference also)
Problem 2: (Frequency-Shift Keyed Signaling)
Consider the FSK signals from class
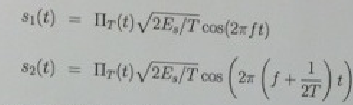
and both signal arc active from time 0 to T, that is r(r) is the rectangular on-off function
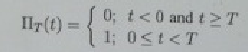
1) Calculate and plot the spectrum of s1(t) and s2(t)
2) Now replace ΠT(t) with P(I), which is a root-Nyquist frequency pulse with a = 0.1. That is. do not chose the time pulse that looks like a sin(x)/x. but the spectral shape from Page 61 of the notes. Sketch both the transmitter side and the receiver side for coherent demodulation.
3) Calculate the spectrum of s1(t) and s2(t) for this case. (Remember and make use of the duality theorem).
4) Can you show if these signals are still orthogonal? If not, is there a frequency spacing that makes them orthogonal?
Part -2:
Consider such a PAM signal
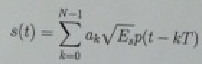
where T is the signaling rate, and E, is the energy per symbol.
In class we chose the at as - I or 41, i.e., binary PAM. but in practice higher levels of
PAM arc used.
1) Use a Nyquist pulse with a = 0.2 can calculate the spectral efficiency. i.e.. the number of transmitted bits per unit bandwidth (or binary PAM, 4-PAM, and I28-PAM
2) The error probability of 2-PAM was computed in the flats on Page 58 in terms of E, and Na. Compute the bit error probability for binary PAM, 4-PAM. and 128-PAM in terms of bit energy Es and Na.
3) In PAM we are sending one symbol per time. rather then two as in DSB. However. nothing prevents us from viewing the even symbols and the odd symbols as two separate channels. Draw a block diagram that interprets this and transmits 64 QAM over the two channels.
4) Now, take your 64 signal points from 3), and eliminate half the points such that for each point its nearest neighbors are removed. Draw the resulting 32-point constellation it is called a 32-dither PAM constellation. Can you compute its bit error rate and compare with those in 2)?
Part -3:
Real Communications Channels
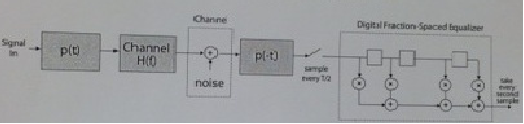
Many practical channels are not distortionless, and we need to "equalize" the channel as discussed in class. The figure below shows the figure from Page 25, but we have added a root-Nyquist transmit and receive filter with, say, a = 1.
This transmission system with the equalizer is shown here:
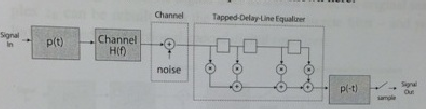
1) What is the bandwidth over which you need to equalize the channel? Determine the delay of the delay elements.
2) Show formally that the receive filter and the tapped-delay line can be interchanged, as shown below, and we can work with this system.What are the delays in the delay elements such that the entire bandwidth of the system is covered. Note that the bandwidth of p(t) is 1 /T.
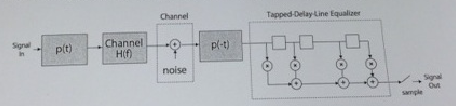
3) Let z(t) be the output of the receiver system. Sample the output at the symbol rate to generate the samples zk = z(kt).
Now, instead of sampling after the tapped delay line, you sample the sign al at the output of p(-t), but sample it at the Nyquist rate, not the symbol rate. Denote these samples by yj.
Write down an expression for yi, and show that if these samples are passed through a discrete digital filter a; shown below, the original samples zk can be rebuilt from the output of this discrete filter - and you have derived the fractional-spaced digital equalizer.