Part A -
Problem 1 -
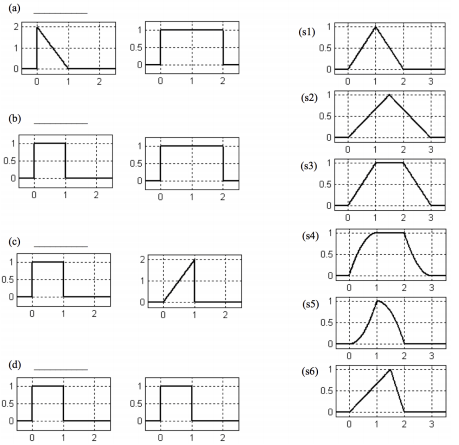
Compute the following convolutions - Since we have unit step functions available to express functions that are 0 for t < 0, you should be able to easily express your answers for parts (a) and (b) a single line, without a giant "conditional statement". Part (c) has three regions; you should still be able to express your answer in one line by employing a difference of unit step functions.
(a) exp(-2t)u(t) * exp(-4t)u(t)
(b) exp(-2t)u(t) * exp(-2t)u(t)
(c) [u(t) - u(t-2π)] sin(t)u(t)
Problem 2 -
For each pair of signals on the left, select the signal on the right that is the convolution of the two signals. Not all of the signals on the right will be used, and some may be used more than once.
Part B -
Problem 1 -
Now that you're getting the hang on an amazing property of transmission lines with sinusoidal signals, we will explore another method of matching called series-stub matching. Consider the below diagram. A 40 Ω transmission line must be matched to an antenna. The antenna is characterized by a 50 Ω resistor in series with a 10/(3π) pF capacitor. The antenna is connected to a feeder transmission line that has impedance of 100 Ω and is exactly one-quarter wavelength long. To match that antenna and feeder line to the 40 Ω power transmission line and eliminate reflections, you connect a series transmission line at the end of the quarter-wave segment. This stub is shorted at the end.
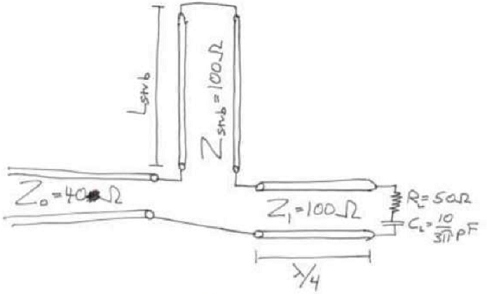
a. What is the smallest length Lstub that produces a perfect match, meaning that any voltage from the generator (the generator is off the left edge of the diagram) does not return to the generator? Your answer should be as a fraction of a wavelength.
b. You designed this circuit for a 3 GHz wi-fi transceiver. What is the voltage standing wave ratio at 3 GHz on the input section of the transmission line (that's the section leading to the generator)?
c. The circuit has been built and is sitting on your lab bench. But your annoying professor just decided to switch to a different frequency, and wants to try out 2 GHz. Since you've taken 3025 and remember a really fun homework assignment, you know that series-stud matching only works at one frequency, so you need to calculate how well it will match at this new frequency. What is the VSWR if you use the same circuit board you've built, but inject 2 GHz instead?
d. This is not part of the homework, but some food for thought: What do you think determines the "bandwidth", i.e. how quickly or slowly the quality of the match falls off as you move away from 3 GHz? Can you think of any ways to either increase or decrease the bandwidth?
Problem 2 -
So you build the circuit in part 1(b). But everything in your design assumed that the transmission line would be lossless. But you've taken 3025 and remember a really fun homework assignment, so you know that board fabrication is never precisely what you designed, anyways. So you decide to take some high frequency measurements and find the following transmission line parameters at 3 GHL: L = 10.1 nH/cm, C = 1.1 pF/cm
a. What is the characteristic impedance?
b. You then realize that you should also measure the losses, too. So with additional high frequency measurements, you calculate that G = 0.014 5/cm, R = 143.5 Ω /cm. What is the characteristic impedance including the losses?
c. What is the propagation constant y?
d. For a transmission line 10 cm long, how much will a 1 V signal attenuate?