Part-1
Q1: Illustrate the radio frequency system of an amplitude modulated transmitter using block diagram. Explain the function of each stage of the transmitter and how is this related to stages connected at the input and output of each stage.
Q2: Using block diagram illustrate an AM modulator explaining the function of each block. Using Multisim or any other relevant software:
a. Produce an AM signal with the following parameters:
Carrier frequency: fc = 100kHz
Message frequency: fm= 800Hz
Modulation index: m=1
b. Detect and reproduce (demodulate) the message signal. Measure the frequency of the detected signal and compare that with the frequency of the message.
Provide screenshots for modulated and demodulated signals with their relevant information
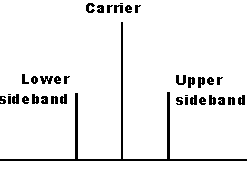
Q3: Figure 1 shows the spectrum of a double sideband full carrier (DSBFC).Calculate the frequencies of the DSBFC spectrum. Suggest a method and present your calculation to detect the lower side band at the output. This should produce a single sideband frequency spectrum knowing that the parameters of the spectrum are:
Carrier frequency: fc = 10kHz
Message frequency: fm= 150Hz
Part-2
Derive a system diagram for a frequency-modulated transmitter and explain the function of each stage
Analyse angle modulation
Q1:Illustrate the radio frequency system of a frequency modulated transmitter using block diagram. Explain the function of each stage of the transmitter and how is this related to the stages connected at the input and output of each stage.
Q2: For the following parameters, use Multisim or any relevant software to:
a. Produce an FM modulated signal:
Carrier frequency: fc = 5kHz
Message frequency: fm= 500Hz
Modulation index: ?=5
b. Analyse the effect of changing the modulation index to ?=2 and ?=8. Discuss the changes resulted in the FM output
Task 3
Draw a block diagram of an AM tuned-radio frequency (TRF) receiver and explain its operation
Tuned Radio Receivers are of the oldest receivers that were used until World War 2. Draw a block diagram for a TRF radio and give an explanation to the function of each stage an the operation of the complete TRF radio.
Task 4
Explain the principle of operation of the superheterodyne receiver
Superheterodyne receiver, that sometimes called superhet, uses frequency mixing principles to convert the received radio frequency signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF). Electronically, the new IF signal can easily be processed than the received radio carrier frequency. Using a block diagram, explain the principle of operation of the superheterodyne receiver and the function of each stage.
Task 5
Explain the necessary arrangements for transceiver operation
Having a transmitter and receiver working separately such as radio station (only transmitter) and home radios (only receiver) is not difficult. Difficulties arises when both transmitter and receiver are joined in one circuit board to obtain a transceiver that transmit and receive signals. Explain the necessary arrangement needed to overcome these difficulties and for the transceiver to operate safely.