Assignment: Nerve Signals
The nervous system is responsible for communication and coordination of all organ systems within a body. To achieve this, the neurons - cells that make up the nervous system - must be able to pass signals from one to another. To understand how a neuron transmits a signal, it is important be reminded of the structure of the neuron. The dendrites receive chemical or electrical signals from the axon terminals of other neurons. The cell body contains the nucleus, lysosomes and ribosomes. Most neurons have a single axon which sends signals to other neurons. These signals are carried down the axon into the axon terminals which are small branches of the axon. The axon terminals form synapses, or connections, with other cells. The space between two nerve cells is called the synaptic cleft.
When a neuron is not transmitting a signal, it is at rest. During this rest period, the cytoplasm just inside of the neuron contains two important molecules: positively charge potassium ions (K+) and negatively charged protein molecules. (A positively charged ion occurs when an atom loses one or more electrons. Negatively charged molecules form when the molecule gains extra electrons.) The cytosol contains more negatively charged protein molecules than potassium ions, so the inside of the neuron is negativeincharge. The fluid just outside of the neuronispositivelycharged. This positive charge is due to the presence of positively charged ions, likesodium(Na+). Thecellmembranestores energy by holding these opposite charges apart. This difference in charge is referred to as an electrical potential. When the neuron is at rest, this difference in charge is referred to as the restingpotential.
Sending a signal through a neuron - Action Potential
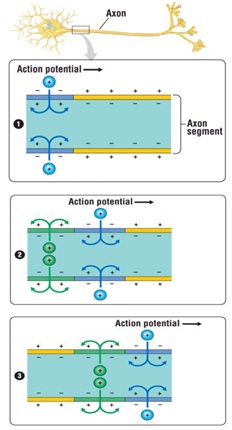
A stimulus (light, sound, touch or the presence of a chemical) can generate an electrical nerve signal by reversing the charges inside and outside of the neuron's membrane. c Action potential occurs when specialized protein channels, called ion channels, open and allow the positively charged sodium ions to diffuse into the cell. This influx of positive ions causes the inside of the cell to become more positive than the outside of the cell. This reversal of charge then triggers the sodium channels to close, blocking the diffusion of Na+. Meanwhile, another type of ion channel opens allowing potassium ions (K+) to diffuse out of the cell. This causes the charge on the inside of the cell to become negative again. The neuron has returned to resting potential.
To transmit the signal throughout the neuron, the action potential must travel the length of the neuron. The changes in charge in one area of the neuron trigger the opening of Na+ channels is membrane just down-stream of the action potential. As a result, an action potential is generated in the adjacent region and is quickly followed by a return to resting potential. The action potential travels down the neuron like dominoes falling over; each reversal in charge triggers the opening of ion channels in the adjacent membrane.
Action potentials are the same no matter what stimulus caused them. Your central nervous system (CNS) can detect different intensity of different stimuli by interpreting the frequency of action potentials traveling down the neuron. For example, if you tap your finger on your desk softly, your CNS will receive fewer action potentials per second than if you tapped your finger very hard.
Passing a signal from one neuron to another - Chemical synapse
If the nervous system is going to function properly, neurons must be able to communicate with each other by passing signals to one another. This occurs at a synapse, or relay point between two cells. The most common type of synapse in the nervous system of animals is chemical synapse. Chemical synapse occurs in the narrow space between the axon terminal of the sending neuron and the dendrite of the receiving neuron.
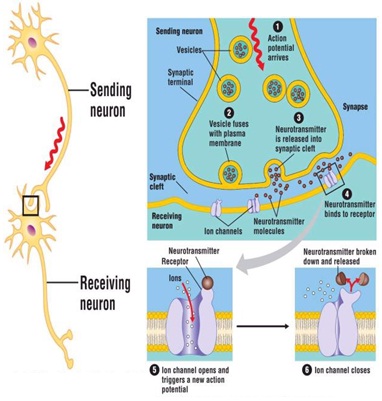
When action potential reaches the axon terminal, it is converted into a chemical signal. This chemical signal comes in the form of a neurotransmitter (a chemical that carries information from one nerve cell to another). Once the action potential arrives at the end of the neuron, it stimulates vesicles containing a neurotransmitter. The vesicle will then fuse with the cell membrane and release the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft using the process of exocytosis. The released neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor molecules, which are proteins attached to ion channels within the membrane of the receiving cell. The binding of the neurotransmitters to the receptor molecules causes the ion channels to open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell. This influx of Na+ ions causes an action potential in the receiving neuron. The neurotransmitter is then either broken down or transported back to the sending neuron to be reused. The absence of neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft causes the ion channels to close and the signal toend.
AnalysisQuestions
Directions: Answer question based on readings
1. What term is used to describe a neuron that is not transmitting asignal?
2. Describe the conditions inside and outside of a neuron during restingpotential.
3. Describe the conditions inside and outside of a neuron during action potential.
4. What causes a neuron to change from resting potential to actionpotential?
5. What causes a neuron to return to a resting potential from an actionpotential?
6. How is a signal transmitted through a singleneuron?
7. What is aneurotransmitter?
8. How are neurotransmitters secreted into the synaptic cleft?
9. How does a neurotransmitter cause an action potential in a receivingneuron?
10. How is the signal between neurons stop?