Assignment: Long-Run Cost
Part I:
Let's go back to the car wash company from an earlier problem set. In calculating the firm's short run costs, we used the following definitions and information:
Q = Output per day = # of cars washed per day
L = Labor = number of workers employed, the only variable input in the short run
K = Capital = number of automated car-wash lines, the only fixed input in the short run Cost of Labor = $100 per worker per day
Cost of Capital = $200 per automated-lines per day
Over the short-run time horizon we analyzed earlier, the firm was stuck with 2 automated lines (K = 2). and could only vary its labor (L).
But now you'll be asked to calculate what the firm's costs would be if it instead were stuck with 3 or 4 automated lines.
1. Using the information provided above, fill in the blanks for the missing entries for TC and ATC assuming the firm has different levels of capital (K). Round answers to the nearest second decimal (i.e., to the nearest penny).
With K = 2 With K = 3 With K = 4
|
Q
|
L
|
TC
|
ATC
|
|
L
|
TC
|
ATC
|
|
L
|
TC
|
ATC
|
|
600
|
18
|
$2,200
|
$3.67
|
|
17
|
|
|
|
16
|
|
|
|
800
|
22
|
$2,600
|
$3.25
|
|
19
|
|
|
|
18
|
|
|
|
1,000
|
28
|
$3,200
|
$3.20
|
|
24
|
|
|
|
23
|
|
|
|
1,200
|
36
|
$4,000
|
$3.33
|
|
33
|
|
|
|
30
|
|
|
2. For the following problems, assume the firm currently has 2 automated lines.
a. Starting from where it is currently, if the firm wants to wash 800 cars per day over a short-run time horizon, its cost per car would be $ _____ . In the long run, the least-cost method of washing that number of cars per day would use _____ automated lines and _____ workers, and the cost per car would be $ _____.
b. In the short run, if the firm wants to wash 600 cars per day, its cost per car would be $ _____. In the long run, the least-cost method of washing that number of cars per day would use _____ automated lines and _____ workers, and the cost per car would be $ _____.
c. Using similar comparisons of cost per car for the remaining output levels, fill in the missing entries in the table below. (Remember that LRTC is the firm's long-run total cost, the total cost of its least-cost input mix for each output level.)
Least Cost Input Mix
|
Q
|
K
|
L
|
LRTC
|
LRATC
|
|
600
|
2
|
18
|
$___
|
$___
|
|
800
|
3
|
19
|
$___
|
$___
|
|
1,000
|
___
|
___
|
$___
|
$___
|
|
1,200
|
___
|
___
|
$___
|
$___
|
d. In the long run, this firm would experience economies of scale until its output level reaches _____ cars washed per day. As its output rises beyond this level, the firm experiences _____ [constant returns to scale | diseconomies of scale]
(Part II follows on next page)
Part II
The diagram below shows cost curves for a pizza place at different quantities of pizzas produced per day (Q). In the short run, the firm has just one fixed input - ovens (K). Each ATC curve shows the firm's cost per unit for different numbers of ovens it might initially have. For example, ATCK = 2 is the ATC curve when the firm has two ovens. The LRATC curve for this firm is also shown.
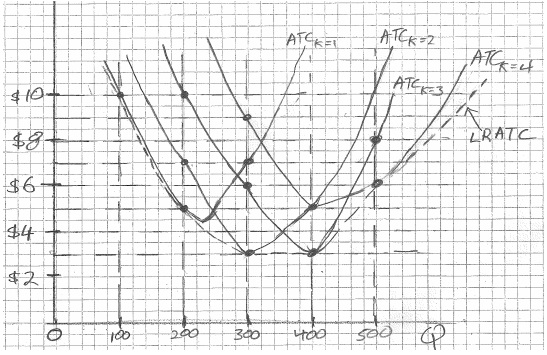
For each of the following questions, answers should be to the nearest whole number.
1. Suppose the pizza place currently has just one oven. Then to produce 300 pizzas per day in the short run, its cost per pizza would be $ _____. To produce 300 pizzas per day in the long run, the firm should use _____ ovens, and its cost per pizza would be $ _____.
2. Suppose the pizza place has been producing 300 pizzas per day for a long time, so it is already using the least-cost method to produce them (i.e., it has the number of ovens to produce Q = 300 at the lowest possible cost). But then it decides to change its output to 400 pizzas per day. In the short run, its cost per pizza at its new output level will be $ _____, but in the long run - after it has time to adjust the number of ovens - its cost per pizza will be $ _____.
3. Suppose the pizza place has been producing 400 pizzas per day for a long time, so it is already using the least-cost method to produce them. But then it decides to change its output to 200 pizzas per day. In the short run, its cost per pizza at its new output level will be $ _____, but in the long run - after it has time to adjust the number of ovens - its cost per pizza will be $ _____.
4. This firm experiences economies of scale over the range of output from 0 to _____, constant returns to scale from _____ to _____, and diseconomies of scale at any output level greater than _____.