Assignment -
Activity 1: Respiratory anatomy
1. The flow chart below follows the pathway a molecule of oxygen takes on its way to the lungs. The terms and letters on the left side of the diagram in red and flowing vertically represent the major organs on this pathway. The blue letters arranged horizontally represent smaller structures within each of these major organs. Use the list of terms below to complete the flow diagram. Space at the bottom is provided for your answers.
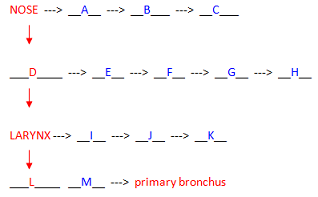
Terms:
- adenoids
- carina
- epiglottis
- external nares
- internal nares
- laryngopharynx
- middle meatus
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- pharynx
- trachea
- vocal folds
- vestibular folds
ANSWER THE FOLLOWING IN COMPLETE SENTENCES
2. Describe 3 ways in which the air that enters the respiratory tract is altered by the time it reaches the lungs.
For each way, cite one anatomical feature of the airways that allow for this change
3. Maggie has aspirated a small piece of candy into one of her primary bronchi. Where might the doctor expect to find this object? Why?
4. Match each region of the lung with the specific airway which supplies it.
____bronchopulmonary segment a. primary bronchus
____lobule b. secondary bronchus
____alveolar ducts and sacs c. tertiary bronchus
____entire lung d. large bronchiole
____lung lobe e. respiratory bronchiole
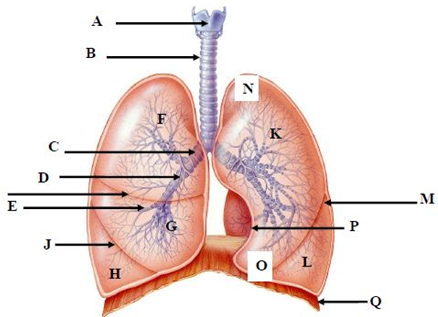
5. Use the diagram below to identify the labeled structures (A-Q).
Activity 2 - Hemogloblin transport of oxygen
Print out the linked graph that shows % saturation of hemoglobin as a function of pO2. Both the X and Y axes are marked at intervals of 10. The O and 60 on each scale have been added to guide you.
Exercise 1
a. Use only the black line on the graph for this first exercise.
b. Fill in the missing numbers on each axis of the graph.
c. Use a ruler to draw vertical lines on the graph at pO2 = 30, 40, 50, 60, 80 mm Hg.
d. Draw horizontal lines across to the Y-axis to determine the % saturation value at each pO2 Use these values to fill in the table below.
|
pO2 (mm Hg)
|
% sat. Hb
|
|
30
|
|
|
40
|
|
|
50
|
|
|
60
|
|
|
80
|
|
e. Use your data to calculate the change in % saturation with the following changes in pO2. For example, for the first change in % sat. Hb, go to the table above and subtract the % sat for 60 mm from that for 80 mm.
|
Change in pO2
(mm Hg)
|
Change in
% sat. Hb
|
|
80 ---> 60
|
|
|
60 ---> 40
|
|
|
50 ---> 30
|
|
f. Looking at the table above, where did the greatest change in % saturation of Hb occur?
between 80 and 60 PO2?
between 60 and 40 PO2? or
between 50 and 30 PO2?
g. What does this tell you about the release of O2 from Hb? Is it greater or lesser as the partial pressure of oxygen in the tissues becomes lower?
h. Why might this effect be a desirable one? What advantage might it provide?
Exercise 2 -
a. Return to the graph and using all three lines, determine % saturation of Hb at pO2 of 25 mmHg.
|
Line
|
% satd. Hb
|
|
Blue line
|
|
|
Black line
|
|
|
Red line
|
|
b. Which line on the graph shows the strongest binding of oxygen to Hb at pO2 of 25 mm?
c. Which line on the graph shows the weakest binding of oxygen to Hb at pO2 of 25 mm?
d. Define the term "affinity" as it relates to the binding of oxygen by hemoglobin.
e. If the black line represents the normal relationship between Hb saturation and pO2, does a shift of the curve towards the right represent an increase or a decrease in affinity of Hb for oxygen?
f. Under conditions in which there is more O2 being consumed, more CO2 being produced and/or a higher temperature in tissues due to greater metabolic activity, would you want Hb to more readily or less readily release oxygen?
g. Which line on the graph would demonstrate the actions of Hb in this situation?
Activity 3 -
1) Match a term to each description
a. atmospheric pressure
b. intrapulmonary pressure
c. intrapleural paressure
_____As it increases over atmospheric pressure, air flows out of the lungs.
_____In healthy lungs, it is always lower than atmospheric pressure.
_____Pressure of air outside the body
_____As it decreases, air flows into the passageways of the lungs.
_____If this pressure becomes equal to atmospheric pressure, the lungs collapse.
_____Rises well over atmospheric pressure during a forceful cough.
2) Match the process to its description
a. external respiration
b. expiration
c. inspiration
d. internal respiration
e. pulmonary ventilation
___period of breathing when air enters the lungs
___alternate flushing of air into and out of the lungs
___exchange of gas between alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood
___period of breathing when air leaves the lungs
___exchange of gases between blood and tissue cell
3) In the following paragraph, select the words that correctly complete each sentence. Either highlight the correct word or cross out the incorrect word.
When the diaphragm contracts, the internal volume of the thorax (increases, decreases), the size of the lungs (increases, decreases), the internal pressure of the lungs (increases, decreases), and air flows (in, out). On the other hand when the diaphragm relaxes, the internal volume of the thorax (increases, decreases), the size of the lungs (increases, decreases), the internal pressure of the lungs (increases, decreases), and air flows (in, out).
4) Match the gas law its the description(s).
a. Boyle's Law
b. Dalton's Law
c. Henry's Law
___If a patient breathes air highly concentrated in oxygen (such as in a hyperbaric chamber), a higher percentage of oxygen will dissolve in the blood and tissues.
___The total atmospheric pressure is due mostly to pressure caused by nitrogen, partly to pO2 and slightly to pCO2.
___Under high pN2, more nitrogen dissolves in blood. The bends occurs when the pressure decreases and nitrogen forms bubbles in tissue as it comes out of solution.
___As the size of the thorax increases, the pressure within it decreases.
5) For each of the three gases below (O2, CO2 and H2O vapor), rank the areas in order of decreasing concentrations. For example, if the concentration of O2 is highest in the alveoli, then that area receives a 1. Then next lowest area would receive a 2, etc. Treat each gas separately.
O2:
___alveoli
___tissue cells
___external atmosphere
CO2:
___alveoli
___tissue cells
___external atmosphere
H2O:
___alveoli
___external atmosphere
6) With increasing altitude, the air becomes thinner, gas molecules are farther apart, so atmospheric pressure decreases. Atop a 10,000 mountain peak atmospheric pressure is 523 mm Hg. Oxygen still accounts for 21% of the total pressure. Calculate PO2 at this elevation. ________mm.
How does this compare to the PO2 at sea level?
What effect would this elevation have on the pressure gradient between alveolar air and alveolar blood - increase, decrease or no change?
What effect would this pressure gradient have on the ability of oxygen to move into blood - increase, decrease or no change? Explain your answer.
Question: 3 assignments. Act 2 has a diagram to reference.
Attachment:- Assignment Files.rar