1. Cartesian Tensor:
Express the following vector identities in index notation and then prove the identities using tensor algebra. (Note: u→ and v→ are vectors, Φ and ψ are scalars, ∇Φ is the gradient of the scalar function Φ, and ∇u→ is the gradient of the vector u→.)
(a) u→ x (∇ x u→) = ½ ∇(u→· u→) - u→ · ∇u→
(b) ∇ x (∇ x u→) = ∇(∇ · u→) - ∇2u→
(c) ∇ · (u→ x v→) = v→· (∇ x u→) - u→· (∇ x v→)
(d) ∇ x (Φu→) = ∇Φ x u→ + Φ(∇ x u→)
(e) ∇2(Φψ) = (∇2Φ)ψ + Φ(∇2ψ) + 2∇Φ · ∇ψ
2. Analysis of Stress:
A 2-D rectangular plate ABCD of size 4-in x 2-in, as shown in the figure, is subjected to the action of body force b→ and tractions applied along its four edges. The plate is in a state of equilibrium and the stress in the plate is given by
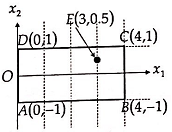
(a) Determine the components of the body force bi
(b) Determine the components of the traction, ti, acting along each of-the four edges of the plate. Sketch the distribution of each component.
3. Analysis of Strain:
Verify if the following 2-D state of (infinitesimal) strain is possible.
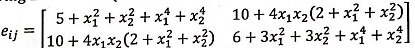
4. Stress-strain relations:
The length of edge (AD)- of a thin skew plate ABCD is 1.0 inch in the original (undeformed) state. Determine the length of the (AD)- and the angle ∠CDA in the deformed state if the plate is subjected to a 2-D constant state of stress as shown. The plate is made of aluminum with material properties of the place is E = 107 psi and v = 0.33.
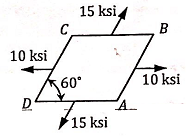
5. Torsion:
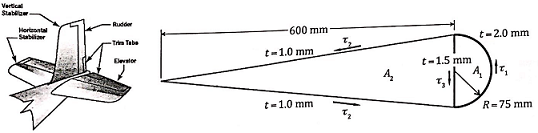
The cross-section of an airplane elevator is shown in the figure below. The thickness is 2.0 mm for the curved leading edge, 1.5 mm for the vertical cord, and 1.0 mm for the straight trailing edge. The elevator is 2 m long and constructed from aluminum alloy with G = 30 GPa. A 40 Nm torque is applied at one end of the elevator. Calculate the total angle of twist at the other end if the cross-section is assumed to be constant throughout its length. Also calculate the magnitude of shear stress in each part of the cross section.
6. 2D Plane Problems:
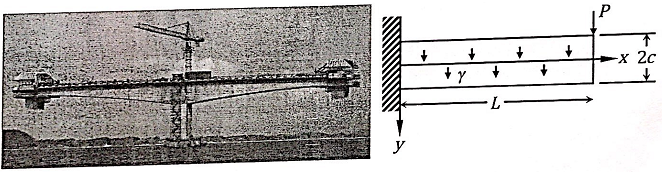
Picture below on the left shows a cantilever bridge under construction. Due to symmetry only the right-half of the bridge is modeled as a cantilever beam and analyzed. For convenience, the beam is assumed to be prismatic (uniform cross-section) with a unit thickness (perpendicular to the paper). The beam is subjected to a concentrated load P at the free end and a uniformly distributed body force γ. Determine the stress σij and the vertical displacement of the centerline (y = 0) of the beam. To simplify the problem, we assume P = 2cLy.
7. 2D Plane Problems:
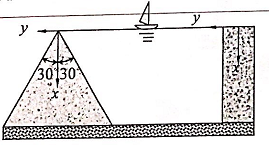
Determine the stresses in the two earth dams as shown, one with a triangular cross-section (a = ±30o) and the other with a rectangular cross-section (width 2c), due to the water pressure and the weight of the dams. The dams are assumed to be tall enough so that the displacement boundary conditions at the bottom of the dams are irrelevant. Assume that the weight density of the dam, yd is three time of the weight density of the water, γw, i.e., γd = 3γw.
8. 2D Plane Problems:
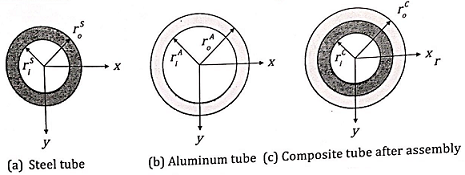
Figures above show (a) a steel tube of inner radius ris and outer radius ros and (b) an aluminum tube of inner radius riA and outer radius roA. At the room temperature, the outer radius of the steel tube, ros, is slightly larger than the inner radius of the aluminum tube, riA, i.e.,
ros - riA = Δ > 0
The two tubes are shrink fit (first by expending the aluminum tube with heat until riA > ros, then insert the steel tube in and let the assembly cool down to room temperature) to form a composite tube, Figure (c) above.
Show in detail (in particular, the boundary conditions) how to determine the stresses, the inner radius, and the outer radius of the assembled composite tube. SET UP THE EQUATIONS, BUT DO NOT SOLVE THEM.
For convenience, assume the followings:
ris = r1, ros ≈ riA = r2, roA = r3
GSteel = 3GAluminum, vSteel = vAluminum = 0.3
9. 2D Plane Problems:
Derive the expressions of displacements ur and uθ for the Airy stress function Φ = r3cos θ.
Assignment Files -
https://www.dropbox.com/s/6z9vhonc2j6biqr/Assignment%20Files.rar?dl=0