problem 1: You may �find parts of this problem similar to the 'Landing on an Alien World' activity. Start by opening the 'Maze Game' activity. You can �find it under Unit 3 on Moodle. When you open it you will be presented with the 'Arena of Pain'. Set it to 'practice' and play with the controls. You will �find that by clicking in the lower-right box you are able to create a vector which controls the motion of the red dot in the arena. Play around with it. In particular, it has three modes: R, V and A. Figure out what they do. We will only use 'practice' mode, but you may find Level 1, Level 2 and Certain Death fun.
a) Use the 'Maze Game' to explore the motion of an object which starts from rest, accelerates to the left and then switches to accelerating down. Sketch a motion diagram for this.
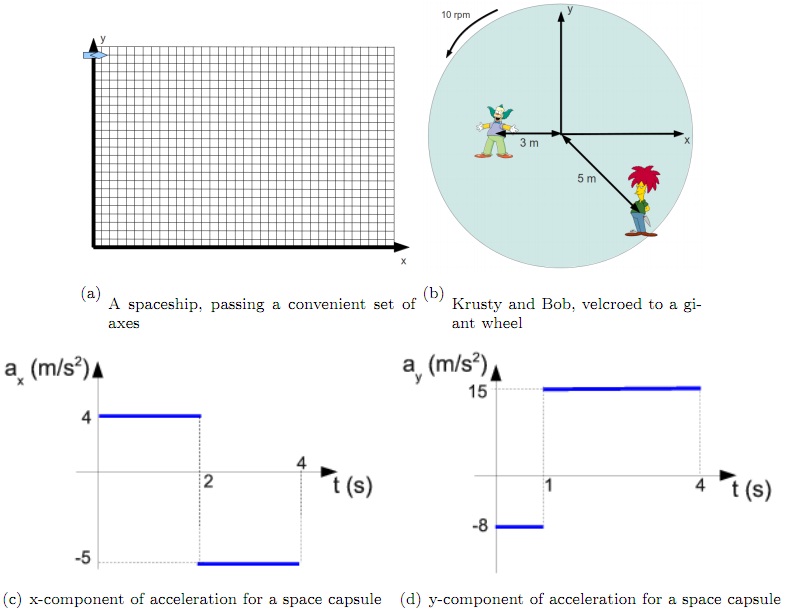
b) We will now do this slightly more precisely. A spaceship is initially at rest at (230m) J near a set of axes that someone conveniently left floating in space here. It is shown in Figure (a) which has a scale of 10 m per square. Reproduce the �figure on graph paper. The spaceship accelerates at 20 m/s2 in the x-direction for 3 s. It then stops accelerating in the x-direction and immediately accelerates at 10 m/s2 in the negative y-direction for 4 s. Draw the motion diagram for the spaceship, to scale, on graph paper.
problem 2: Krusty the Clown and Sideshow Bob have covered themselves in velcro, and shot themselves out of a large cannon so that they stick to a big rotating velcro wheel. Krusty is now stuck to a point 3.00 m from the center of the wheel while Bob is stuck to the other point 5.00 m from the center. The wheel is initially rotating counter clockwise at 10.0 rpm. Conveniently a set of axes is suspended just in front the wheel (Krusty asked for axes, like the ones you would use to chop wood, so that he and Bob could chase each other with them in the usual wholesome entertainment he is known for. Unfortunately, the set designer misunderstood.) The axes don't rotate with the wheel.
a) Find out Krusty's and Bob's angular velocities, in radians per second.
b) Find out Krusty's and Bob's tangential velocities.
c) Find out Krusty's and Bob's accelerations.
d) At t = 0 the wheel begins to speed up at a uniform rate. Over 10.0 s it goes from rotating at 10.0 rpm to rotating at 20.0 rpm. Graph the angular velocity vs. time for the wheel during this time, complete with scales on the axes.
e) At t = 5.00 s Krusty is passing the x-axis. Find out his total acceleration vector at this instant.
problem 3: This is a group problem. Only hand in one copy for the whole group. Please do not attach it to the assignment of any of the group members; hand it in separately. After completing it you will also submit feedback via a moodle poll to tell me how well your group has worked together. Your individual mark on this problem will be based on your group's success at doing the problem but also on your group members assessments of your contribution to the learning of the group while they worked on it. This problem would take a fairly long time to do by yourself, but if you divide up the work it should not take terribly long. While you don't need Maple to do this problem, much of this problem will be much easier if you do it in Maple. The two graphs in Figure (c) and Figure (d) show the acceleration vs. time for a space capsule in the process of maneuvers to dock with a space station. The origin of the coordinate system is at the space station. The capsule starts at t = 0 with:
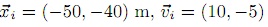
m/s.
a) Draw (complete with scales on the axes) the vx vs. t graph and the vy vs. t graph for the capsule for times from t = 0 to t = 4 s.
b) Sketch (no scales required on the axes) the x vs. t and y vs. t graphs for the capsule for times from t = 0 to t = 4 s.
c) What is the velocity (don't forget that it is a vector) of the capsule at t = 2s? What is its velocity at t = 2s? How about t = 4s?
d) What is the position of the capsule at each of t = 2s and t = 4s?
e) What is the average acceleration of the capsule over the whole time interval from t = 0 to t = 4s?
f) prepare the functions x(t) and y(t) for the whole time interval t = 0 to t = 4s (it might help you to decide on an approach that the functions will be "piecewise continuous"). Plot the trajectory (y vs. x) for the capsule. By far the easiest way to do all of this will be in Maple, but it could also be done fairly easily in a spreadsheet.