Lab - Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
Theory:
By sampling the discrete in time Fourier transform in the frequency domain we can obtain the discrete Fourier series (DFS). The DFS can then be extended to finite- duration sequences which results in a new transform, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT). The numerical computation of the DFT for long sequences can be prohibitively time consuming. As a result, algorithms were developed to compute the DFT efficiently and is collectively known as the fast Fourier transform (FFT).
Prelab Assignment:
Lab:
1. Compute the DFS coefficients of the following periodic sequences using the DFS definition and then verify your answers using MATLAB.
a. x1~(n) = {4,1, -1, 1} N = 4
b. x2~(n) = {2, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0}, N = 8
c. x3~(n) = {1, 0, -1, -1, 0}, N = 5
d. x4~(n) = {0, 0, 2 j, 0, 2j, 0), N = 6
e. x5~(n) = (3, 2, 1), N = 3
2. Let X(ejω) be the DTFT of a finite lenght sequence
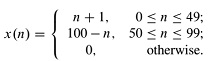
a. Let
y1(n) = IDFS10-point[X(ej0), X(ej2Π/10), X(ej4Π/10),......,X(ej18Π/10) ]
Determine y1(n) using the frequency sampling theorem. Verify your answer using MATLAB.
b. Let
y2(n) = IDFS200-point[X(ej0), X(ej2Π/200), X(ej4Π/200),......,X(ej398Π/200) ]
Determine y2(n) using the frequency sampling theorem. Verify your answer using MATLAB.
c. Comment on your results in parts (a) and (b).
3. Consider the following finite-length sequence:
x(n) = { sinc2{(n - 50)/2}, 0 ≤ n ≤ 100;
{ 0, else.
a. Determine the DFT X(k) of x(n). Plot (using the stem function) its magnitude and phase.
b. Plot the magnitude and phase of the DTFT X(ejω) of x(n) using MATLAB.
c. Verify that the above DFT is the sampled version of X(ejω). It might be helpful to combine the above two plots in one graph using the hold function.
d. Is it possible to reconstruct the DTFT X(ejω) from the DFT X(k)? If possible, give the necessary interpolation formula for reconstruction. If not possible, state why this reconstruction cannot be done.
4. Let a finite-length sequence be given by:
x(n) = { 2e-0.9|n|, -5 ≤ n ≤ 5;
{ 0, otherwise.
Plot the DTFT X(ejω) of the above sequence using DFT as a computation tool. Choose the length N of the DFT so that this plot appears to be a smooth graph.
5. Plot the DTFT magnitude and angle of each of the following sequences using the DFT as a computation tool. Make an educated guess about the length N so that your plots are meaningful.
a. x1 (n) = (0.6)|n|[u(n + 10) - u(n - 10)].
b. x2(n) = n(0.9)n, 0 ≤ n ≤ 20.
c. x3(n) = cos(0.5Πn) + j sin(0.5Πn), 0 ≤ n ≤ 50.
d. x(n) = {1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2, 1}.
↑
e. x(n) = (-1,-2,-3,0,3,2,1).
↑
6. A 512-point DFT X(k) of a real-valued sequence x(n) has the DFT values:
X(0) = 20 + jα; X(5) = 20 + j30; X(k1) = -10 + j15; x(152) = 17 + j23;
X(k2) = 20 - j30; X(k3) = 17 - j23; X(480) = -10 - j15; x(256) = 30 + jβ;
And all other values are known to be zero.
a. Determine the real-valued coefficients α and β.
b. Determine the values of the integers k1, k2 and k3.
c. Determine the energy of the signal x(n).
d. Express the sequence x(n) in a closed form.
7. Compute the N-point circular convolution for the following sequences. Plot their samples.
a. x1(n) = sin(Πn/3)R6(n), x2(n) = cos(Πn/4)R8(n); N = 10
b. x1(n) = cos(2Πn/3)RN(n), x2(n) = sin(2Πn/4)RN(n); N = 32
c. x1(n) = (0.8)nRN(n), x2(n) = (-0.8)nRN(n); N = 10
d. x1(n) = nRN(n), x2(n) = (N - n)RN(n); N = 10
e. x1(n) = (0.8)nR20x2(n), x2(n) = u(n) -u(n-40); N = 10
8. Let x(n) be a uniformly distributed random number between [-1,1] for 0 ≤ n ≤ 106.
Let
h(n) = sin(0.4Πn), 0 ≤ n ≤ 100
a. Consider the conv function, determine the output sequence y(n) = x(n)*h(n)
b. Consider the overlap and save method of block convolution along with the FFT algorithm to implement high speed block convolution. Using this approach, determine y(n) with FFT sizes of 1024, 2048 and 4096.
c. Compare these approaches in terms of the convolution results and their execution times.