Reaction Engineering Coursework Assignment
Learning Objectives -
- To gain an understanding of how to derive mathematical models to describe the operation of batch, semi-batch and continuous flow reactors.
- To gain an understanding of how to use mathematical models, by employing a numerical method, to find the performance characteristics of chemical reactors such as the product distribution.
Skills Outcomes -
- Ability to analyse modes of process operation of chemical reactors.
- Ability to solve problems related to reactor design and employ appropriate numerical techniques to perform quantitative analysis of reactor performance.
Assignment Description -
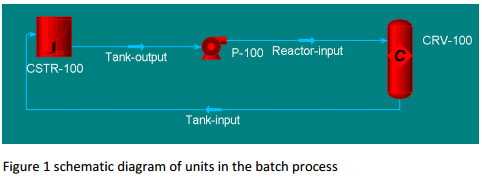
1. Consider the batch process shown in Figure 1: a stirred tank (CSTR-100) is connected in series with a reactor (CRV-100) containing a mass per unit volume, W, of solid catalyst. The reactants and products of the reaction process are all liquids which are circulated via a pump (P-100). There is no feed to this closed-loop system and no product is withdrawn. No chemical reaction process occurs in the absence of catalyst hence none occurs in the stirred tank. Assume that initially the tank and reactor contain only reagent A. You may also assume:
1. The tank and the reactor are instantaneously well mixed,
2. There is no change in fluid density accompanying the reaction process,
3. The volume of the liquid in the connecting pipe work may be neglected,
4. There is no resistance to mass transfer in the reactor (at the interface between the solid-catalyst particles and the liquid).
The reaction scheme is A ? B → C
The first reaction is first order with respect to A in the forward direction, with rate constant, k1f, and first order with respect to B in the reverse direction with rate constant, k1b. The second reaction is irreversible and first order with respect to B with rate constant k2.
For a solid-catalysed process an appropriate batch-reactor performance equation for reagent A is:
t/CA0 = V/W0∫X_A dXA/-r'A
Here, t, is elapsed time, CA0 is the initial concentration of reagent A, V is the volume of liquid in the reactor, XA is the fractional conversion of reagent A and r'A is the rate of appearance by chemical reaction of reagent A in moles per unit mass of solid-catalyst per unit time.
(i) What are the units of the rate constants?
(ii) The volume of the stirred tank is V1 and the volume of the void-space in the reactor is V2. By performing a material balance derive performance equations describing the time dependence of the concentration of reagent A and products B and C in the stirred tank. Explain the meaning of any terms you introduce.
(iii) Similarly derive performance equations describing the time dependence of the concentration of reagent A and products B and C in the reactor. Explain the meaning of any terms you introduce.
(iv) Using the performance equations you have derived in parts (ii) and (iii), investigate how the distribution of products CB/CC in the tank and in the reactor varies with time depending on (a) the ratio V2/q where q is the volumetric flow-rate, (b) the ratio V1/V2, (c) the ratio k1f/k1b and (d) the ratio k1f/k1b. Assume that CA0 is constant, 1 mole/litre, and that V2 and W are constant. In your assignment report you must provide the evidence on which you have based your investigation and hence your conclusions. This includes output from any numerical approach you use to solve the performance equations such as the Euler method implemented in an Excel spreadsheet. You must decide on an appropriate range of ratio values to use for (a) - (d) and then justify the values you have selected in your write-up. You should not write more than 2500 words for part (iv) excluding table captions and figure captions.
(v) Provide a brief summary to your report (150 word limit).