Questions:
Q1) Suggest an example of a decision from your own experience which you feel is best treated as a decision without probabilities. What principle of choice would seem appropriate?
Q2) In formulating a view of a decision, how can we handle the feelings we nave about probabilities which are not supported by objective relative frequency evidence? What is meant by "complete ignorance of the probabilities of the possible futures"?
Q3) Comment on the following argument: "Any principle of choice ought to select alternatives which would maximize expectation for some set of probabilities. If there is an alternative for which there exists no set of probabilities which would make it the expectation maximizing alternative, then no principle of choice should lead to its selection."
Q4) Suppose you know that the instructor in a certain course gives only the grades A, B, or C, He makes you the following offer: If you can guess the grade which he has already assigned you, he will raise it by one letter (except in the case of A); if you guess wrong, he will lower it by one letter; and if you choose not to guess at all, you will of course receive the assigned grade. Explain your choice.
Q5) Apply the various principles of the choices to the following matrix. The number in the matrix are costs.
|
18
|
18
|
10
|
14
|
|
14
|
14
|
14
|
14
|
|
5
|
26
|
10
|
10
|
|
14
|
22
|
10
|
10
|
|
10
|
12
|
12
|
10
|
From a new matrix from the one above by taking each number, adding 2, and multiplying the result by 3. Again apply the principles of choice. What does this suggest with respect to value measurement?
For this, the rows correspond to strategies and the columns correspond to scenarios; use the following criteria:
a) Expected value
b) Risk profile dominance (stochastic or deterministic)
c) Most likely outcome
d) (Uniform) Average over outcomes
e) Maximin
f) Maximax
g) Hurwicz
h) Minimax regret
i) Expected regret
Q6) For the decision tree below, first convert it to a table like in Q5. Label strategies and scenarios. Then solve for the best strategy using the following criteria:
a) Expected value
b) Risk profile dominance (stochastic or deterministic)
c) Most likely outcome
d) (Uniform) Average over outcomes
e) Maximin
f) Maximax
g) Hurwicz
h) Minimax regret
i) Expected regret
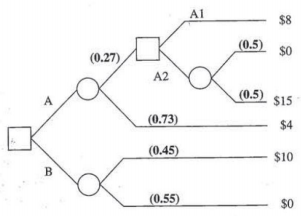
(Hint: This tree should look familiar)
Q7) "Prescribed Fire" case study
PRESCRIBED FIRE
Using fire in forest management sounds contradictory. Prescribed fire, however, is an important tool for foresters, and a recent article describes how decision analysis is used to decide when, where, and what to burn. In one example, a number of areas in the Tahoe National Forest in California had been logged and were being prepared for replanting. Preparation included prescribed burning, and two possible treatments were available: burning the slash as it lay on the ground, or "yarding of un-merchantable material" (YUM) prior to burning. The latter treatment involves using heavy equipment to pile the slash. YUM reduces the difficulty of controlling the burn but costs an additional $100 per acre. In deciding between the two treatments, two uncertainties were considered critical. The first was how the fire would behave under each scenario. For example, the fire could be fully successful, problems could arise which could be controlled eventually, or the fire could escape, entailing considerable losses. Second, if problems developed, they could result in high, low, or medium Costs.
Questions -
1. What do you think the U.S. Forest Service's objectives should be in this decision? In the article, only one objective was considered, minimizing cost (including costs associated with an escaped fire and the damage it might do). Do you think this is a reasonable criterion for the Forest Service to use? Why or why not?
2. Develop an influence diagram and a decision tree for this situation. What roles do the two diagrams play in helping to understand and communicate the structure of this decision?
Source: D. Cohan, S. Haas, D. Radloft and R. Yancik (1984) "Using Fire in Forest Management: Decision Making under Uncertainty." Interfaces, 14, 8-19.
Attachment:- Assignment File.rar