problem 1: Determination of Catalyst Particle Size.
Our packed bed reactor conducts the gas phase reaction A → R at P = 10 atm and T = 336oC and gives 90% conversion using a feed that consists of pure A. However, our favorite catalyst sales person guarantees that in the absence of pore diffusional resistance, this same reaction will proceed on his new and improved porous catalyst (Deff = 2 x 10-6 m3/m cat-s) with a rate equation given by:
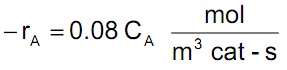
This rate is much better than what we can do now with our current catalyst. However, the new catalyst is rather expensive since it is formulated of compressed kookaburra droppings and it is sold by weight versus catalyst volume. Given the above information, what diameter of catalyst spheres should we order from our catalyst sales person?
problem 2: Catalyst Effectiveness Factor for a Long Cylindrical Catalyst.
Consider diffusion and first-order reaction A → P occurring in a long cylindrically-shaped porous catalyst with a radius of r = R under isothermal conditions in the presence of an inert gas. The concentrations of reactant A and product P are low enough that the local
flux can be described in terms of Fick’s law so that NA = -De dNA/dr.
a) Assuming that CA = CA(r) and that –rA = k CA (mol/m3cat-s), set up a shell balance with all units (use SI units) and show that the governing mass balance equation is:
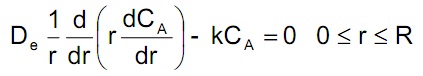
What other assumption or assumptions was (were) made to arrive at this equation?
b) prepare the boundary conditions at the pellet center r = 0 and the pellet surface r = R for the case where the surface of the catalyst is exposed to a gas whose concentration is CA = CAS in the absence of any external gas film mass transfer resistance.
c) Transform the above mass balance equation in dimensionless form by introducing the following dimensionless variables for the concentration and radial coordinate, respectively,
u = CA/CAS and ρ = r/R
Show that when these groups are introduced, that the dimensionless group Φ2 = R2 k/De emerges from this analysis. Show the units of each term in this parameter and that it is indeed dimensionless.
d) Solve the above equation and associated boundary conditions to obtain an expression for the dimensionless concentration profile for specie A. (Note: This solution will be expressed in terms of the modified Bessel function of the first kind).
e) Using the solution for the dimensionless concentration profile for specie A derived in step d above, obtain the expression for the catalyst effectiveness factor by both of the methods discussed in class, i.e., integration of the concentration profile and differentiation of the derivative. Show that the effectiveness factor is η= I1(2Φ)/[ΦoI0(2Φ)] where I0(x) and I1(x) are modified Bessel functions of the first kind of order 0 and 1, respectively.
f) Prepare a table that lists the expressions for the dimensionless concentration profiles and catalyst effectiveness factors for slab, cylinder and spherical catalysts.
(g) prepare an Excel program that computes the dimensionless concentrations as a function of the dimensionless coordinates for slab, cylindrical and spherical pellets using Φ = 0.5, 1, 2, 5 and 10 and draw three separate graphs. Use at least 50 values of the dimensionless coordinate so you get smooth curves.
h) Using your expressions for the catalyst effectiveness factor, create a chart of catalyst effectiveness factor versus the Thiele modulus.
problem 3: Effectiveness Factor in Slurry Hydrogenation
The liquid phase hydrogenation of hydrocarbons, such as olefins to paraffins, is accomplished by bubbling hydrogen gas (specie A) through a liquid phase containing suspended porous catalyst particles. The gas dissolves in the liquid, diffuses into the catalyst pores, and reacts there at an active site. The reaction is first-order with respect to the limiting reactant (hydrogen) and has a diffusion-free rate constant of k = 0.1 m3/m3 catalyst-s. The goal is to achieve a reaction rate in the reactor so that
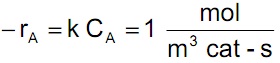
From vapor-liquid equilibrium data, the Henry’s law constant for the solubility of hydrogen gas in this hydrocarbon is estimated to be
HA = PA/CA = 0.1m3 liquid-atm/mol H2
where pA is the partial pressure of hydrogen gas and CA is the concentration of dissolved hydrogen gas in the liquid. The effective diffusivity of dissolved hydrogen gas in the liquid-filled pores of the catalyst is estimated to be:
De = 2 x 10-9 m3/m catalyst-s
a) If we wish to insure that pore diffusion effects do not result in inefficient use of the catalyst, and if operation is to be performed at atmospheric pressure, what size of suspended catalyst particles should be used?
b) What hydrogen pressure must be used if we want to get the required rate of reaction using 3 mm catalyst pellets in a packed bed reactor?