Consider the planar linkage shown below. The crank (link with length R) will turn counter-clockwise with constant angular velocity. The slider will experience a force of 100 N directed to the left. Your task is to write a program that calculates the required input torque and the magnitude of the pin reaction forces for two revolutions of the input link. You will then use your program to determine how changing the dimension H changes the average magnitude of the pin reaction forces at pins A, B and C (refer to the free-body diagram for the location of these pins).
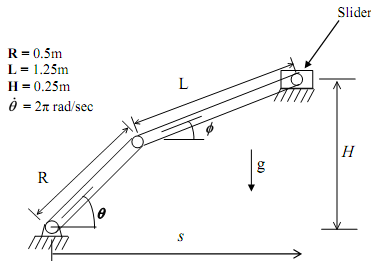
The first task is to determine the coordinates Φ, s given θ. The constraint equations that must be satisfied are:
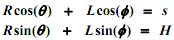
You are required to solve these equations using Newton's method. The next task is to solve for the time derivatives of Φ, given θ(constant). Equations (1) and (2) may be differentiated to obtain the following linear systems of equation in the unknowns. You may use the MATLAB "\" operator to solve these.
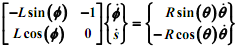
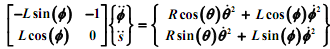
The next step is to draw the free-body diagrams and write the corresponding dynamic equations. Following is the free-body diagram. Note that we are neglecting friction on the slider.
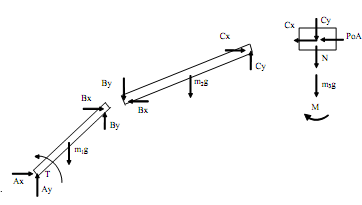
The resulting dynamics equations may be cast in matrix form as
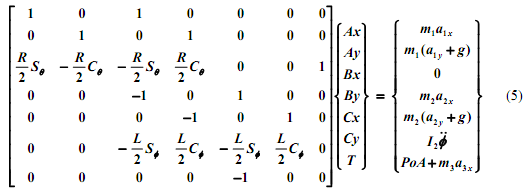
where m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 25 kg, m3 = 10 kg and I2 = m2 L2/12
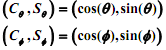
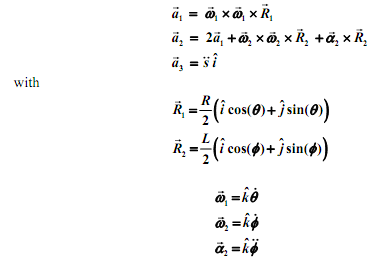
You may use the MATLAB cross function to obtain the above cross products. Note that the accelerations are known functions of the derivatives of the three coordinates.
Turn in a brief report containing the following:
(i) title page
(ii) introduction and objectives
(iii) program design (choices for functions)
(iv) results including plots (labeled) of simulation results for the base case
(v) include a plot displaying the average value of the magnitude of the pin reaction forces over the complete cycle vs. H for the range -0.7≤H≤0.7
(vi) discussion of results including conclusion for part (v)
Code:
m.file for kinemt
function [x,v,a] = kinemt(R,L,H,theta,xo,omega,alpha)
phi = xo(1);
s = xo(2);
% constraint equations
f(1) = R*cos(theta)+L*cos(phi)-s;
f(2) = R*sin(theta)+L*sin(phi)-H;
while f*f'>1.0e-8
Jac = [-L*sin(phi) -1;
L*cos(phi) 0];
dx = -Jac\f';
phi = phi+dx(1);
s = s+dx(2);
f(1) = R*cos(theta)+L*cos(phi)-s;
f(2) = R*sin(theta)+L*sin(phi)-H;
end
x = [phi,s]';
Jac = [-L*sin(phi) -1;
L*cos(phi) 0];
rhsv = [R*sin(theta)*omega -R*cos(theta)*omega]';
v = Jac\rhsv;
rhsa = [R*cos(theta)*omega^2+L*cos(phi)*v(1)^2;
R*sin(theta)*omega^2+L*sin(phi)*v(1)^2];
a = Jac\rhsa;
m.file for loader
function [system, rhs] = loader(R,L,H,theta,x,omega,alpha,v,a,PoA);
m1 = 10;
m2 = m1*L/R;
m3 = m1;
I2 = m2*L^2/12;
g = 10;
R1 = 0.5*R*[cos(theta) sin(theta) 0]';
omega1 = [0 0 omega]';
temp1 = cross(omega1, R1);
a1 = cross(omega1, temp1);
R2 = 0.5*L*[cos(x(1)) sin(x(1)) 0]';
omega2 = [0 0 v(1)]';
alpha2 = [0 0 a(1)]';
temp2 = cross(omega2,R2);
a2 = cross(omega2,temp2)+cross(alpha2,R2)+2*a1;
a3 = [a(2) 0 0]';
system = zeros(7);
rhs = zeros(7,1);
system(1,1) = 1;
system(1,3) = 1;
rhs(1) = m1*a1(1);
system(2,2) = 1;
system(2,4) = 1;
rhs(2) = m1*(a1(2)+g);
system(3,1) = 0.5*R*sin(theta);
system(3,2) = -0.5*R*cos(theta);
system(3,3) = -system(3,1);
system(3,4) = -system(3,2);
system(3,7) = 1;
system(4,3) = -1;
system(4,5) = 1;
rhs(4) = m2*a2(1);
system(5,4) = -1;
system(5,6) = 1;
rhs(5) = m2*(a2(2)+g);
system(6,3) = -0.5*L*sin(x(1));
system(6,4) = 0.5*L*cos(x(1));
system(6,5) = system(6,3);
system(6,6) = system(6,4);
rhs(6) = I2*a(1);
system(7,5) = -1;
rhs(7) = PoA+m3*a3(1);
main m.file for project
R = 0.5;
L = 1.25;
H = 0.25;
omega = 25;
alpha = 0;
PoA = 1000;
index = 0;
for H = -0.7:0.05:0.7
H
for k = 1:721
theta(k) = (k-1)*2*pi/360;
if k == 1
xo = [0 L+R]';
else
xo = [phi(k-1) s(k-1)]';
end
[x,v,a] = kinemt(R,L,H,theta(k),xo,omega,alpha);
phi(k) = x(1);
s(k) = x(2);
phid(k) = v(1);
sd(k) = v(2);
phidd(k) = a(1);
sdd(k) = a(2);
[system,rhs] = loader(R,L,H,theta(k),x,omega,alpha,v,a,PoA);
forces = system\rhs;
torq(k) = forces(7);
pin1(k) = sqrt(forces(1)^2+forces(2)^2);
pin2(k) = sqrt(forces(3)^2+forces(4)^2);
pin3(k) = sqrt(forces(5)^2+forces(6)^2);
end
index = index+1;
HH(index) = H
p1m(index) = max(abs(pin1));
p2m(index) = max(abs(pin2));
p3m(index) = max(abs(pin3));
p1a(index) = max(abs(pin1));
p2a(index) = max(abs(pin2));
p3a(index) = max(abs(pin3));
end
plot(HH,p1m,'r',HH,p2m,'g',HH,p3m,'b')
pause
plot(HH,p1a,'r',HH,p2a,'g',HH,p3a,'b')
pause
subplot(211)
plot(theta,phi)
subplot(212)