Assignment - Gradually Varied Flow Profiles and Numerical Solution of the Kinematic Equations
Objectives
1. Evaluate and apply the equations available for the description of open channel flow
2. Solve the equations governing unsteady open channel flow
3. Apply the equations of unsteady flow to practical flow problems
Question 1 - Gradually Varied Flow Profiles
Water is flowing in a long prismatic channel of trapezoidal cross section with base width 3.5 m and the side slope 2.2 (Hor.): 1 (Ver.). The channel is made of rough concrete whose Manning roughness is 0.018.
The channel is conveying a steady flow rate of 5 + (2xn1)m3/s
The bed slope of the channel is 0.00035 + (0.0001xn2)
Where, n1 is the second last digit and n2 is the last digit in your student number.
For example if your student number is 10005007648 then
Q = 5 + (2x4) = 13m3/s
S0 = 0.00035 + 0.001x8 = 0.0012
The downstream end of the channel drops vertically into a reservoir (discharges freely into the air). Note that for a free outfall the water depth closely approximates critical flow depth. Take alpha as being 1.1 (α = 1.1).
Your task:
a) Use the direct step method, and the equation below to compute the water surface profile upstream of the outfall.
Δy/Δx = S0-S-f/1-F-2R where FR = √α V/ √(gy-)
b) Plot the water depth against distance
c) Plot the longitudinal bed, normal depth, critical depth, water surface and energy line over the length of this profile. (All on the same set of axis e.g. Fig 5.22 Chadwick)
d) Include sample hand calculation in the report
Hints:
- The size of the step is up to you.
- Use of computers for this task (Matlab, Excel etc is encouraged)
- When computing the water surface profile you should stop just short of normal depth
- The Froude number and critical depth for a trapezoidal channel are different to that of a rectangular channel (e.g. need average depth (y) instead of max depth (y) in FR)
Question 2 - Kinematic Wave Model
Background
You have been asked to investigate the flow behaviour of a large sporting field subjected to a short duration high intensity storm rainfall event.
As part of the process you will develop a computer simulation of the water depths and flow rates for a specified rainfall pattern. The kinematic wave approximation is a simple form of one dimensional flow model, which is deemed sufficient for this task.
The Sporting Field
For study purposes it has been deemed sufficient to represent the behaviour of the sporting field with a one dimensional hydraulic model, in effect reducing the two dimensional sporting field to a unit flow width running down the predominant slope direction. Basically, you will estimate water depth and flow rate per unit width at constant interval.
The length of the carpark area is determined by the last digit of
L = 120 + N1 x 10
For example if your student number was 01121584
L = 120 + NLast x 10
L = 90 + 4 x 10
L = 160 m
For the purpose of this study you may assume a constant value of Manning roughness n across the sporting field. You should justify your choice.
The specifications of the car park are as follows:
Manning n = based on your research
Field slope is uniform with 0.1% drop over length L
Freely draining at the downstream end.
Design Inflow
The model will be used to simulate the flood behaviour subjected to an extreme rainfall event. An example of such event is as below which occurred in Toowoomba on 10th of January 2011. The rainfall hyetograph chosen for this study (Figure1) is from the weather station at Eastern Valley.
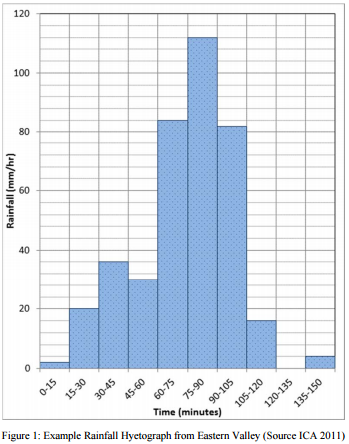
For simplicity it will be assumed in this study that the surface was already saturated at the start of the storm and that the continuing rainfall loss will be zero.
Model Specifications
Model Type: 1-dimensional kinematic wave approximation Backward difference in x and Forward difference in time t
Boundary Conditions:
Initial condition (t = 0): q = 0 and y = 0 for all x
Upper boundary (x = 0) q = 0 for all t.
Grid Step Sizes
Maximum distance step Δx <= 10 m
Time step: Must satisfy Courant stability condition
Your Task -
1) Complete the tutorial problems 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 and 5.4 in Module 5. You will find full solutions of first three questions in the study book that will help you to solve 5.4.
2) OPTIONAL: If you are not confident about your answer to 5.4 you may submit your working (formulas/equations) to the examiner using the link provided on study desk before proceeding with the numerical scheme. Your examiner will be able to guide you through.
3) Build your model (using any programming language or spreadsheet) for solving the kinematic wave equations for computing depth and flow rate resulting from the storm events. You must configure your model according to the specifications above.
4) Validate your mathematical model by modelling the runoff under steady rainfall (constant rainfall depth) and compare results with the theoretical results for steady rainfall. The analytical procedure for theoretical results has been discussed at the end of this problem (The section Model Validation) You are required to check all three conditions.
5) Modify the model to accommodate the design storm hyetograph. Then use this program to calculate water depth and flow rate at uniform distance interval dx along the unit width channel for he given storm event.
6) Write up all equations, model development, validation, results and discussion in a report format.
Attachment:- Assignment File.rar