Analysing a simple system
An accelerometer is a dynamic sensor capable of a vast range of sensing. Accelerometers are available that can measure acceleration in one, two, or three orthogonal axes. They are typically used in one of three modes:
- As an inertial measurement of velocity and position;
- As a sensor of inclination, tilt, or orientation in 2 or 3 dimensions, as referenced from the acceleration of gravity;
- As a vibration or impact (shock) sensor.
Accelerometers have applications in industry and science. Accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems of missiles and aircraft, to detect and monitor vibration in machinery and to detect seismic activity. They are used in tablet computers and smartphones so images are always upright on the screens, and in video game controllers to detect the position of the device and provide game input, as well as pedometers that count the number of steps taken and distance travelled.
Most accelerometers are Micro-Electro-Mechanical Sensors (MEMS). The basic principle of operation behind the MEMS accelerometer is the displacement of a small proof mass etched into the silicon surface of the integrated circuit and suspended by small beams. Consistent with Newton's second law of motion (F = ma), as an acceleration is applied to the device, a force develops which displaces the mass. The support beams act as a spring, and the fluid (usually air) trapped inside the IC acts as a damper, resulting in a second order lumped physical system.
Consider the accelerometer shown below:
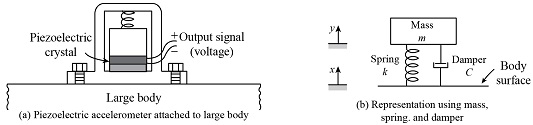
In this figure:
- x is the position of the large body, with its rest position given by x = 0.
- The mass m represents the inertial mass within the accelerometer.
- The height of mass m above its reference level is called y. The reference level is chosen such that when accelerometer is at rest, y = 0.
- The voltage output, V, would be proportional to the change in the difference between x and y due to piezoelectric effect.
Section 1: Mathematical Analysis of System
1. Draw a free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on the inertial mass, m
2. Let z(t) = y(t) - x(t). From the earlier description, diagrams and the laws of Physics, show that the motion of the accelerometer can be described by the LCCDE (linear constant-coefficient differential equation) below:
d2z(t)/dt2 + C/m.dz(t)/dt + k/m.z(t) = d2x(t)/dt2 (1)
Equation (1) shows that the output response depends on the acceleration of the large body.
The accelerometer is a damped second order system. It is common to express the homogenous second order DE for such a damped system as
d2z(t)/dt2 + 2ζωndz(t)/dt + ω2nz(t) = 0
where ζ is the damping ratio and mn is the undamped resonant frequency
3. From equations (1) and (2), determine expressions for ζ (the damping ratio) and ωn (the natural frequency) in terms of the parameters m, k and C
4. Determine the characteristic equation and eigenvalues (characteristic values) for this system based on equation (2) above.
5. From the answer to part 4, determine the natural response of the system for the following cases:
a. 0 < ζ < 1
b. ζ = 1
c. ζ > 1
Consider an accelerometer with the following parameters:
m = 4.3 x 10-6 kg
k = 508 N/m
6. Determine ωn for this accelerometer and the required value of C for ζ = 1
Note: Complete and clear working is required for all answers for this section.
Section 2: System analysis using Matlab
In this section, the system responses should be analysed using Matlab. Refer to the document "A Brief MATLAB Guide" in order to understand how to represent LTI systems in Matlab, and hence how to determine impulse response, step response and frequency response of systems. MATLAB is installed in the engineering computer labs.
Using the commands given in the Guide, analyse the response of the system using the following m and k parameters given in Section 1 and C value calculated in question 6:
7. Plot the impulse response and step response of the system (for 1 millisecond duration and time ‘step size' of 10 nanoseconds) using the impulse and step functions. Include all plots (properly labelled) in your submission.
8. Determine the frequency response from 0 Hz to 20,000 Hz using the freqs command. Plot the magnitude and phase response over this frequency range. Hint: Use frequency ‘step size' of 100 Hz.
Hint 1: You can plot all 4 graphs in one go using a 2 x 2 matrix of plots using subplot(22n), where n determines which of the 4 subplots gets used.
9. Determine the magnitude response at ωn. Determine the frequency of the -3dB point(where magnitude = 1⁄√2). Hint: Use the ‘data cursor' tool on the plot of the magnitude response. It shows the x and y values of the plot as you move along the curve.
10. Discuss the response of the system. Why do the impulse and step responses have that particular shape? How well will this accelerometer fulfil its purpose of a vibration sensor? Based on the frequency response, what limitations will there be on its usefulness?
Note: The function of a vibration sensor is to provide an accurate measurement of vibrations over a range of frequencies.
11. Repeat the analysis above (steps 7 - 9) for the following damping ratios
a. ζ = 0.5
b. ζ = 2
Hint 2: It would be more efficient to put all the necessary commands into a script file (a .m file) so you can edit the parameters and then run all the commands at once.
12. Based on the results of the Matlab analysis above, which of the 3 values of damping ratio would be best for application as a vibration sensor. Justify your selection.
Part 3: Investigation of State Space Analysis Techniques
In this section, the task is to research the state space analysis approach to signals and systems design and investigation and to produce a concise (~1500 - 2500 words) research report describing your findings.
You should explain what the state space analysis approach is (the final chapter in the textbook is a good starting point), its advantages and disadvantages, and what types of problems it is appropriate for. You should identify in the literature particular classes of problems that state space analysis techniques have been applied to, provide a review of the methods that have been proposed to address those problems and the outcomes realised. You should also include a section on the state space analysis of the accelerometer analysed in Parts 1 and 2. Finally you should provide a conclusion contrasting the different methods researched and discussing how useful you think state space analysis approaches are to the researched problem area.