Problem: Bloomberg Businessweek Case in the News
Maybe March Madness Boosts (Rather Than Kills) U.S. Productivity I n 2006 an innovation was unleashed on the teeming, college-basketballhungry masses that promised to unshackle us from the fear of watching NCAA March Madness tournament games at work. The Boss Button allowed basketball fans at work to switch between the live stream of a game and a phony financial statement or innocuous spreadsheet. Most of us don't get paid to watch basketball. This year workers in the United States have so far spent 10.5 million hours watching NCAA tournament games while on the clock. If, as many have argued, all this time is completely unproductive and costs the U.S. economy $1.7 billion a year, bosses should rightfully crack down on tournament viewing at work. These productivity analyses, however, are not based on hard data about how the tournament actually affects people's behavior. They're just multiplying the time spent watching games and picking brackets by the average hourly rate paid to workers. But let's think about the March Madness effect more broadly. What if, rather than employees just sitting at their desks glued to their monitors, March Madness gets people talking to their colleagues, walking around the office, and generally creating the kind of camaraderie and information flow that companies need to flourish? Communication is the most important thing that happens at work, even if it's not work related. At a major pharmaceutical company, for example, our research showed that a 10 percent increase in face-to-face communication with people on other teams increased sales more than 10 percent, which translates into hundreds of millions of dollars.
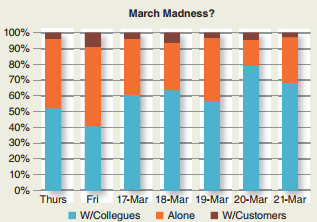
To give this question a proper examination, then, I'll dig into data collected at my own early-stage tech company, Sociometric Solutions. We're still relatively small, with fewer than 10 people, but this is a good sample to start with. We collected data on ourselves using Sociometric Badges (wearable sensor ID badges) to measure how our interaction time changed during the first two days of the NCAA tournament. Then we compared these two days with data from earlier in the week, as well as a representative Thursday and Friday from previous weeks. To recap, the Sociometric Badges measure who talks to whom, how people talk to each other, how they move around, and where people spend time. Data on individuals are never shared with employers, and the badges are used on an opt-in basis, with dummy badges that don't collect data provided to people who don't want to participate. OK, now let's get to the data: I must admit, I was quite surprised when I saw these numbers. While the results are not statistically significant, more interaction actually occurred the first day of the tournament (March 20) than every other day that week.
The second day of the tournament (March 21) saw a similar level of interaction. We can also see that the first two days of March Madness have much higher interaction levels than the typical Thursday and Friday. This increased interaction is important. Rather than indicating we're being unproductive, these results argue that we're more productive in the long term thanks to March Madness. As we've seen in many organizations, more interaction within a tightly knit group yields higher performance and higher job satisfaction through increased trust and the development of a shared language. So there you have it: March Madness does not reduce productivity. In fact, it may increase it. In that spirit, I'd like to propose an updated Boss Button for 2015. Instead of hiding the live stream, this Boss Button will call your boss over to your desk to watch the game with you. Because, as the data show, we all should be getting paid to watch basketball. Source: Ben Weber, "Maybe March Madness Boosts (Rather Than Kills) U.S. Productivity, Bloomberg Business Week, March 27, 2014. Used with permission of Bloomberg L.P. Copyright © 2014. All rights reserved.
Questions for Discussion: 1. Besides March Madness, what other events might disrupt work at the office?
2. How can organizations control the disruptive effects of such events?
3. If disruptive events also have the positive side effect of increasing communication, how can organizations create a culture in which these events are appreciated for their positive effects?