While comparables provide a useful starting point, whether this acquisition is a successful investment for KKP depends on Ideko's post-acquisition performance." What does this statement mean?
How can a firm measure the post-acquisition performance of a firm it is acquiring before that performance occurs?
As a result of preliminary conversations with ldeko's founder, you have income and balance sheet information for the current fiscal year shown in Table 19.1. Ideko currently has debt outstanding of $4.5 million, but it also has a substantial cash balance. To obtain your first estimate of Ideko's value, you decide to value Ideko by examining comparable firms.
A quick way to gauge the reasonableness of the proposed price for Ideko is to compare it to that of other publicly traded firms using the method of comparable firms introduced in Chapter 9. For example, at a price of $150 million, Ideko's price-earnings (P/E) ratio is 150,000/6939 = 21.6, roughly equal to the market average PIE ratio in mid-2005.
It is even more informative to compare Ideko to firms in a similar line of business. Although no firm is exactly comparable to Ideko in terms of its overall product line, three firms with which it has similarities are Oakley, Inc., Luxottica Group, and Nike, Inc. The closest competitor is Oakley. which also designs and manufactures sports eyewear. Luxor¬tica Group is an Italian eyewear maker, hut much of its business is prescription eyewear; it also owns and operates a number of retail eyewear chains. Nike is a manufacturer mprecroofspe cialty sportswear products, but its primary focus is footwear. You also decide are Ideko to a portfolio of firms in the sporting goods industry.
A comparison of Ideko's proposed valuation to this peer set, as well as to the average firm in the sporting goods industry, appears in Table 19.2. The table not only lists PIE ratios, hut also shows each firm's enterprise value (EV) as a multiple of sales and EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Recall that enterprise value is the total value of equity plus net debt, where net debt is debt less cash and invest¬ments in marketable securities that are not required as part of normal operations. Ideko has $4.5 million in debt, and you estimate that it holds $6.5 million of cash in excess of its working capital needs. Thus, Ideko's enterprise value at the proposed acquisition price is 150 + 4.5 - 6.5 = $148 million.
At the proposed price, Ideko's PIE ratio is low relative to those of Oakley and Luxottica, although it is somewhat above the P/E ratios of Nike and the industry overall. The same
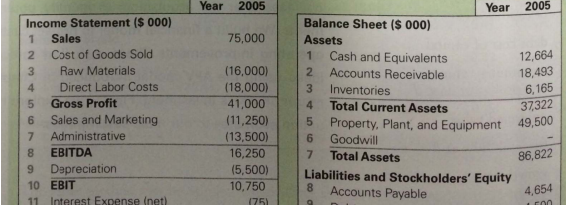
can be said for Ideko's valuation as a multiple of sales. Thus, based on these two measures, Ideko looks "cheap" relative to Oakley and Luxottica, but is priced at a premium relative to Nike and the average sporting goods firm. The deal stands out however, when you com¬pare Ideko's enterprise value relative to EBITDA. The acquisition price of just over nine times EST TDA is below that of all of the comparable firms as well as the industry average. Idekc'L, low EBITDA multiple is a result of its high profit margins: At 16,250/75,000 = 21.7% its EBITDA margin exceeds that of all of the comparables.
Whit- Table 19.2 provides some reassurance that the acquisition price is reasonable compared to other firms in the industry, it by no means establishes that the acquisition is a good investment opportunity. As with any such comparison, the multiples in Table 19.2 vary- Atbstgntially. Furthermore, they ignore important differences such as the operating efficiency and growth prospects of the firms, and they do not reflect KKIrs plans to improve ldeko's operations. To assess whether this investment is attractive requires a careful analysis both of the operational aspects of the firm and of the ultimate cash flows the deal is expected to generate and the return that should be required.