1. In 1997 Egghead Computers ran a chain of 100 retail stores all over the U.S. Consider one type of computer sold by Egghead. Demand for this computer at each store on any given week was independently and Normally distributed with a mean demand of 200 units and a standard deviation of 30 units per week. Inventory at each store is replenished directly from a vendor with a 9 week lead-time.
At the end of 1997, Egghead decided it was time to close their retail stores, put up an internet site and begin to fill customer orders from a single warehouse.
2. By consolidating the demand into a single warehouse, what will be the resulting standard deviation of demand per week for this computer faced by Egghead? Assume Egghead's demand characteristics before and after the consolidation are identical. Choose the closest answer.
a) 90
b) 212
c) 300
d) 900
e) 6363
3. Egghead takes physical possession of inventory when it leaves the supplier and grants possession of inventory to customers when it leaves Egghead's shipping dock. In the consolidated warehouse scenario, what is the average inventory in-transit (inventory that has been shipped by the supplier, but not yet received by Egghead)?
a) 90,000 units
b) 10,000 units
c) 15,245 units
d) 200,000 units
e) 180,000 units
f) 250,000 units
5. A company wants to standardize two of its products to take advantage of product pooling. Under which demand conditions will the standardization be most effective from the standpoint of reducing required safety stock?
a) If demand for the two products is somewhat positively correlated.
b) If demand for the two products is perfectly positively correlated.
c) If demand for the two products is uncorrelated.
d) If demand for the two products is negatively correlated.
e) The benefits of pooling do not rely on the underlying correlation.
6. A company is operating a continuous review (Q, ROP) inventory system where demand per day is normally distributed, the lead time from a supplier is 4 days, and the company currently keeps sufficient safety stock to maintain a service level of 98%. Which of the following actions will reduce required safely stock the most.
a) Reduce required service level to 90%.
b) Reduce lead time from the supplier by 50%.
c) Reduce the standard deviation of demand per day by 50%.
d) Reduce the average demand per day by 10%
FURNITURE STORE (Questions 7-9).
You are the store manager for a furniture store. One of your products is a study desk. This desk comes in two colors: maple and cherry. Weekly demand for each desk color follows a Normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation 50. The demands for the two colors are independent. You order inventory replenishments once per week (using a periodic review inventory control system), the lead-time from your supplier is 3 weeks and your supplier is quite reliable, i.e., you always receive your entire order in three weeks.
7. Suppose your order up-to level (M) is 400 for maple desks. After receiving your weekly delivery from your supplier at the beginning of a week you note that you have 250 units of the maple desk on-hand, 100 maple desks still on-order and no maple desks backordered. How many maple desks will you order this week?
a) 0
b) 50
c) 100
d) 150
e) 200
f) 250
8. What order up-to level (M) should you choose for cherry desks if the objective is to minimize inventory while maintaining a 98.5% in-stock probability? Choose the closest number.
a) 200
b) 300
c) 400
d) 500
e) 600
f) 700
9. Suppose that you estimate that it is 50 times more costly to have a unit backordered in a week than it is to hold one desk for one week. What should be your target in-stock probability if you wish to minimize your expected holding and backorder costs? Choose the closest number.
a) 50%
b) 75%
c) 90%
d) 95%
e) 98%
f) 99%
g) 99.5%
h) Cannot be determined with these data.
10. Mt. Kinley is a strategy consulting firm that divides its consultants into three classes: Associates, Managers, and Partners. The firm has been stable in size for the last 20 years. There has been - and are expected to be- 200 Associates, 60 Managers, and 20 Partners in steady state.
The work environment at Mt. Kinley is very competitive. After four years of working as an Associate, a consultant goes "either up or out"; that is, becomes a Manager or is dismissed from the company. Similarly, after six more years, a Manager either becomes a Partner, or is dismissed from the company. As a policy, the company recruits MBAs as Associates; no hires are made at the Manager or Partner level. A Partner stays with the company for another 10 years - thus having a total career of 20 years with the company.
a) On average, how many new MBAs does Mt. Kinley need to hire every year to maintain the status quo.?
b) On average, how many Associates are dismissed per year?
c) What is the probability that a new hire will become a Partner (as opposed to being dismissed after 4 years or 10 years)?
11. An assembly line is used to produce laptop computers. The assembly process consists of 10 tasks, whose time requirements and precedence relationships are provided below. An operations analyst has provided the solution on the right with 5 work stations and tasks assigned to the stations as indicated. Show your work.
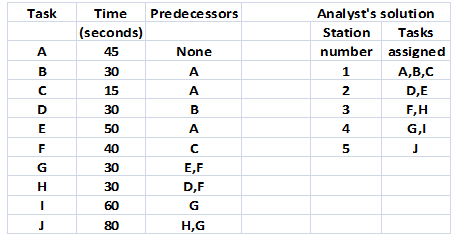
a) Given the solution found by the analyst, what is the maximum output rate attainable by the line, measured in laptop computers per hour?
b) Using the analyst's solution, what is the efficiency of the line if it is operated with a cycle time of 95 seconds?
c) Using the analyst's solution, what is the daily output of the line if it is operated for 8 hours per day (assume no breaks) and cycle time of the line is 100 seconds?
d) Suppose that management wants to set the cycle time to 85 seconds. Find an assignment of tasks to work stations as well as the fewest number of workstations to obtain this desired cycle time.
12. A hospital buys two types of special forms (Form A and Form B) from a local printing company. The hospital uses 20,000 copies per year of Form A at a cost of $0.20 each. 14,000 copies per year is the usage rate of Form B and each such form costs $0.60. Holding costs are based on a 25 percent annual interest rate. The fixed cost of placing an order for either form-type is $100.
a) Find the optimal (EOQ) order sizes and the corresponding annual ordering and holding costs for each form-type assuming they are ordered separately.
b) The hospital is considering an ordering policy where exactly 2 orders per year are placed with the printer and both form-types would be ordered at the same time. The company has estimated the fixed order cost of such an ordering policy for two item-types in a single transaction to be $130 per order. Compute the annual ordering and holding costs of this type of ordering policy.
c) The hospital also purchases disposable surgical kits from a supplier for $400 per kit. Once a kit has opened and used, it is thrown away. The hospital's weekly usage of kits is normally distributed with a mean of 50 and standard deviation of 10. The lead time for delivery of kits once ordered from the supplier is 4 weeks. If the hospital wants to maintain a cycle service level of 98%, what would be the reorder point for a continuous review inventory system?
13. A manufacturing company has decided to lease a special machine from a machine tool supplier, and the type of machine has historically experienced failure of a certain critical part. The supplier has offered the following arrangement to the manufacturer. The supplier will maintain spare units of the critical part for the manufacturer's exclusive use during the period of the rental agreement. Each unit of the spare part reserved by the manufacturer will cost the manufacturer $400, payable at the beginning of the lease agreement. Furthermore this "reservation" cost (an option!) is based on the number of units reserved, and not on the number of units actually needed by the manufacturer. If the manufacturer uses fewer spare part units than are reserved, she receives no rebate on unused reserve units. If the manufacturer actually needs more spare part units than are reserved, the supplier will supply them at a cost of $1000 per unit. The machine is very critical to the manufacturer's business, and so spare parts will always be acquired when needed.
The demand distribution for the part over the lifetime of the rental agreement is:
# units needed Probability
15 .10
20 .30
25 .30
30 .15
35 .10
40 .05
a) What is the probability that additional spare parts will need to be obtained if 20 are reserved
b) What is the sum of the cost of reserving spare parts plus the expected cost of obtaining additional spares if needed, when if 20 spare units are reserved?
c) What are the unit costs of reserving too many (Cs), and not enough (Cu) to be used in the Newsvendor model? Briefly explain your reasoning for your choices
d) What is the optimal number of spare parts to be reserved by the company?
14) Environment Recycling, Inc. must clean up a large automobile tire dump under a state environmental cleanup contract. The tasks, normal duration times (weeks), minimum durations, costs to reduce task times, and predecessor relationships are as follows. Each crash cost is the cost to reduce the corresponding task time per week. Any given task cannot have its time reduced below its "Minimum Time". Thus, for example, task C cannot be reduced below 6 weeks.
|
Activity
|
Predecessor(s)
|
Normal Time(weeks)
|
Minimum Time (weeks)
|
Crash Cost -
per week
|
|
|
A
|
none
|
5
|
4
|
$350
|
|
|
B
|
A
|
12
|
10
|
600
|
|
|
C
|
A
|
7
|
6
|
300
|
|
|
D
|
none
|
6
|
5
|
400
|
|
|
E
|
B,D,C
|
8
|
6
|
500
|
|
|
F
|
D
|
3
|
2
|
200
|
|
|
G
|
D
|
3
|
2
|
150
|
|
|
H
|
E
|
4
|
3
|
200
|
|
|
I
|
F,G,H
|
6
|
5
|
400
|
|
a) What is the critical path and the project completion time using normal task times?
b) If the state wants to complete the project 3 weeks early while spending the least amount of money to do so, which tasks should be reduced and what would be the corresponding cost?