problem 1: A manager of a financial institution you work for manages a portfolio of shares with a value of 20 million $ and standard deviation 16%. The manager wants to use contracts future index in order to modify the characteristics or features of its portfolio but asserting unfamiliar with this market it comes to see you for advice. Submitting him the table array subscripts you know that it is possible to prepare future contracts for a maturity of 6 months. Assume that the covariance between futures on an index and the portfolio is similar as the covariance between this index and portfolio. Each of the future is on 100 x index. Considering finally that r annual risk-free interest rate is 5% and that the covariance among the futures price is 0.002.
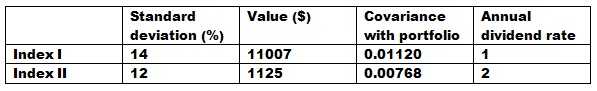
a) Compute the β of the portfolio against each of the indices.
b) Number of futures on index I you require to hold to cover the portfolio?
c) Numberof futures on index II need to hold you for the β of portfolio are 0.5?
d) What minimum deviation for the portfolio is it possible to achieve by using the two indices futures?
problem 2: VALUES OF FUTURES AND FORWARD CONTRACTS
We consider a contract term G and a forward F both written on a similar assets underlying S. We suppose as well that the 2 contracts were written at the time t0 and come ripe in time T (t0 < T). For each of the problems, consider be at time t where t0 ≤ t ≤ T. By convention Ft, Gt and St will designate the price of the instrument at the time t ∈ [t0 T], the increment on the time index is of a day (thus, t + 1 means that we are a day after time t) and marking-to-market is completed daily.
a) describe what is meant by the price of the contracts, F and G? Your answer should be detailed and account of the various values of the parameter t.
b) Assume that t > t0. Would how much you be willing to pay to hold the F contract? How many Calculator for the G contract?
Note: No supposition on the rate of return of an asset without risk can't be done. Assume that however that the market trades bonds z.ro coupon for all maturities.
Suppose from now that the return on assets without riesque is constant at the daily continuous rate r.
c) where the costs (u) and (q) revenues linked to the holding of assets are proportional to its value, the price of the contract F can be expressed usually by Ft = e (c−y)(T −t) St
where c, the cost of detention, is given is given by r - q + u and there is the convenience yield. In the same way that r can be interpreted as the opportunity cost of not investing 1 unit in the asset without risk for 1 day, interpret the rate u, q, c and y.
d) Use your answers to the below problem d) for interpreter (in words) equation (1) when
i) The asset S is crude oil;
ii) The asset S is the exchange rate $CAD/USD
You should first define and make assumptions (realistic) on the PARAMETEES of the EQUATION.
problem 3: Term structure of interest rate
We seek to find out the interest rate term structure (that is, the zero rate curve coupons or equivalently the yield curve) implied by the price that the market assigns to the bonds (supposed to non-risk) presented in table below. To answer this problem, you'll have to interpolate certain values; use then the conventions in the book of Hull. As well use the convention that the composition of the rate (annual) is continuous. We are September 3, 2013 and the convention for the days is current/current.
a) We often supposed that the interest rate r is constant. Draw under this hypothesis the term structure when r = 10.5%. What can be said then about the forwards rate?
b) Name two utilities which make it essential for a Manager to have a view of the structure term of interest rates that is as just as possible.
c) From the data in table below, on a same graph structure the rate futures interest and the forwards rate starting in 3 months to maturity 3 years. That can be said about current rate levels to those anticipated in 3 months?
d) Comparative analysis rates you made to the previous problem does in a context where the investors in the bond market have a preference for liquidity?
Your response should take into account the assumption made determining rates forwards.
e) an FRA is a contract traded for fixing the rate of interest for a specified future period.
Whereas the FRA are evaluated supposing that rates forwards will be made, additional information on the term structure is therefore available in prices which are traded these contracts. Trace the sub-issue c interest rate term structure) by including the data in table below. Atention, we use the convention of Hull for the specialization of the FRAs, namely that the flows included in the cash flow to the maturity of the contract are composed according to a rate reflecting the duration of the loan, but that the rate of the discount factor consists in continuous. The maturity of an FRA is the time T1 and time T2 - T1.
Index: Knowing the rate zero-rT1 and rT2 for T1 and T2 maturity you know how to deduct the RT1, T2 forward for this period rate. This similar formula permits you to express one of the zero coupon rates on the basis of the latter and RT1, T2.
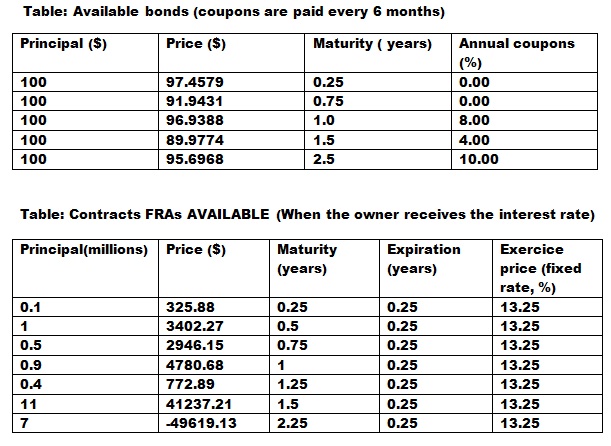
problem 4: SWAPS
a) We are 3 September 2013 and you have a swap contract rate of interest for you receive floating rate and pay a fixed rate to 13.25% over a period of 3 months for a principal of $ 1 million (fixed and floating rates are composed of 3 months, however the discount rate composition is continuous). The payments are SWAP frequency of 3 months and payment. The most recent took place the same day. The swap matures December 3, 2014 and you want to know the value of your contract. To do this, use the data in table above. If you need to discount factors and know the forward rates, using the term structure of Interest derived problem 3 e-rate.
b) A currency swap has a remaining life of 18 months. This swap involves an exchange of interest rate 9% on a £ 15 million against 6.8% of interest of 25 million CAD once a year. The Forward structures of interest in Canada and the UK are expected to flat rate. If the SWAP traded today, the interest rate would be shared by 4% and 8% in CAD Books. All rates are continuous composition. The current exchange rate (CAD/Book) is 1623.
i) Determine the value of the swap from the party paying pounds?
ii) How the exchange rate must he change for the SWAP is of no value?
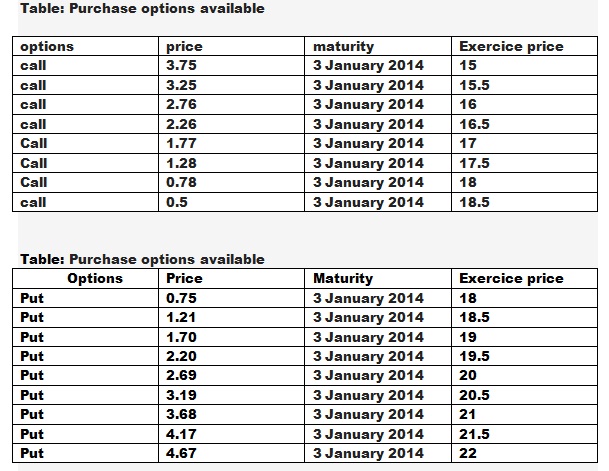
problem 5: Properties of options on stocks
Your parents proud of your entry to the master in finance, you have a gift for the occasion and you 230 offer their shares in the company INC. We are 3 September 2013 and prepare your budget for the next quarter. No dividends are anticipated in the next 6 months for your actions. You want to diversify your portfolio and you consider the options (vanillaEuropean) data in tables shown below.
a) The market for fixed income securities is fluctuating too much, you don't want to speculate relatively to the interest rate without risk but nevertheless you know that zero-coupon bonds three months P (0, 0.25) and 6 months P (0, 0.5) are sold respectively $ 0.98 and $ 0.93. Reprove in this context the put-call parity for options 4 months maturity.
Note: Use the convention book Hull for the term structure of interest rates.
b) With the information collected on the options you consider, is it possible to find out the fair will share of your portfolio?
If so, what is it? If not, what (s) information (s) Extra (s) do you need?
c) Based on the data available options to tables below, what is the maximum price you would pay to buy a forward contract with an exercise price of $18.25 and maturity of four months? At what minimum price would you sell such a contract?
d) After evaluating your budget, you find out that you need additional cash of $ 4000 for January 3, 2014. Unfortunately you cann't invest more. From only your stock portfolio and the options available to tables below, build an investment strategy which will ensure that income .
e) For each exercise price of $ 16 and $ 21, build and assess two investment type butterfly spread strategies.
f) Strategies type butterfly spread for strikes K1 < K2 < K3 and maturity T can be used as an approximation of the probability that the market assigns to the event today that the price of the underlying is K2 time T (called state probability). describe in your own words why it is so. Give the limits of the approximation according to K1 and K3. Finally what can you say about the anticipated probabilities that the market share of the firm ends INC. $ 16 and $ 21 to 3 January 2014 ?
a) We are in the context of binomial trees to a stage where the price of an asset Sº can only go to Su or down to Sd between time t0 and t1 ( prepare T:= t1-t2 ). In class you derived from a portfolio consisting solely of assets and an option on the assets, a synthetic relative probability p if the asset increases in value. This probability can be seen as a neutral appreciation i investor to risk in relation to that asset increases in value and expected returns (continued) risk-free rate r of an investment asset .
formally,
E(I)[ S t1 ] = Sºexp( r T)
i) Based on you only equation (2 ) re-derive p as a function of S0, Su, Sd and r .
ii) Determine the yield an investor I require an investor in O option on the asset?
iii) What argument will be that investors A and I attribute the same value W option?
b) We are still in a world of two periods, but this time the active S0 can take the following respective period Su, S0 or Sd with probability ( in a risk neutral world ) pu , pe and pd (pu + pe + pd = 1). In short, the value of the asset may go up, stay the same or go down. Always from Equation 2 to derive an expression pu. What conclusion can we then take about the risk neutral probabilities?
c) Using a binomial tree at 5 knots, determine a fair price (in USD) of a put option on the U.S. USD 6 months of maturity and exercise price of 0.8000 euro. You know the current exchange rate USD/EURO is 1.3206 and volatility 17%, the exchange rate USD/EURO is 1.3333 and volatility 13%, the risk-free interest rate (continuous) DACUSD and EURO are respectively 3%, 5% and 7%