Question 1.
Initiative D
Shakeit Ltd is considering investing in a new wonder drug for motivating belligerent university students which has an estimated life-span of three years. Shakeit Ltd has determined the following discrete probability distributions for net cash flows generated by the contemplated investment.
Period One (000s) Period Two (000s) Period Three (000s)
Probability Cashflow Probability Cashflow Probability Cashflow
0.10 $ 1200 0.20 $ 1400 0.20 $ 1600
0.15 $ 1260 0.15 $ 1505 0.20 $ 1760
0.25 $ 1323 0.20 $ 1618 0.30 $ 1936
0.30 $ 1389 0.30 $ 1739 0.15 $ 2130
0.20 $ 1459 0.15 $ 1870 0.15 $ 2343
Assume the probability distributions of cash flows for future periods are independent. Also assume that the after-tax risk-free rate is 6 per cent. The proposal will require an initial outlay of $3.75 million
1. Calculate the Expected Value of the Net Present Value.
The Expected Value of the probability distribution of possible net present values is:
(Assuming there is no causal relationship between cash flows from one period to another - I.e. Assumption of Independence.

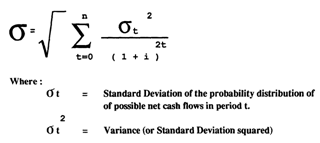
2. Determine the Standard Deviation about the Expected Value.
Under the assumption of serial independence of cash flows for future periods the Standard Deviation of the probability distribution of net present values is -
3. If the total distribution is approximately normal and assumed continuous, what is the probability of the net present value being zero or less?
The expected value and the standard deviation of the probability distribution of possible net present values give us a considerable amount of information with which to evaluate the risk of an investment proposal.
If the probability distribution is approximately normal, we are able to calculate the probability of a proposal providing a net present value of less or more than a specified amount.
The probability is found by determining the area under the curve to the left or to the right of a particular point of interest.
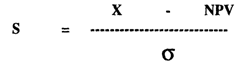
To determine this probability, we first calculate the difference between zero and the expected value for the project. To standardise this difference, we divide it by the standard deviation of possible net present values.
This formula is:

4. What is the probability that the net present value will be greater than zero?
5. What is the probability that the present value index will be 1 or less?
6. What is project's current present value index?
7. What is the probability that the present value index will be greater than 1.5?
If the probability distribution is approximately normal, we are able to calculate the probability of a proposal providing a net present value of less or more than a specified amount. The probability is found by determining the area under the curve to the left or to the right of a particular point of interest.
To determine this probability, we first calculate the difference between zero and the expected value for the project. To standardise this difference, we divide it by the standard deviation of possible net present values.
This formula is:
Question 2.
Lumber Ltd is evaluating a new machine with a life of 2 years. The machine costs $3,000 and future after-tax cash flows depend on demand for the company's products. The tabular illustration of a probability tree of possible future cash flows associated with the new saw is given below:
|
Year 1
|
|
Year 2
|
|
Branch
|
|
Initial
|
Net
|
|
Conditional
|
Net
|
|
|
|
Probability
|
Cash
|
|
Probability
|
Cash
|
|
|
|
P(1)
|
Flow
|
|
P(2/1)
|
Flow
|
|
|
|
|
->
|
0.25
|
1000
|
|
1
|
|
0.45
|
1500
|
->
|
0.25
|
1500
|
|
2
|
|
|
->
|
0.5
|
2000
|
|
3
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
->
|
0.4
|
2000
|
|
4
|
|
0.55
|
2500
|
->
|
0.2
|
2500
|
|
5
|
|
|
->
|
0.4
|
3000
|
|
6
|
a) What are the joint probabilities of occurrence of the various branches?
b) If the risk-free rate is 10 per cent, what is (i) the net present value of each of the 6 complete branches; and (ii) the expected value and standard deviation of the probability distribution of possible net present values?
c) Assuming a normal distribution, what is the probability that the actual net present value will be less than 0 (zero)? What is the significance of this probability?
Question 3.
Discuss the major differences between the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT): Does one outperform the other?