problem 1)a) Food products company is contemplating the introduction of revolutionary new product with latest packaging to replace existing product at much higher price (A) or moderate change in composition of existing product with new packaging at a small increase in price (B) or a small change in the composition of existing product except the word ‘New’ with a negligible increase in price (C).
Three possible states of nature or events are (i) high increase in sales (P), (ii) nochange in sales (Q), and (iii) decrease in sales (R). The marketing department of company worked out the payoffs in terms of yearly net profits for each of the strategies of the events (expected sales). This is represented in the adjoining table.
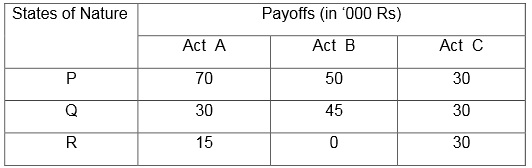
(i) Minimax Regret Criterion
(ii) Laplace Criterion
(iii) Hurwicz (assume that α = 0.6)
(b) Mr John buys perishable commodity at Rs 5 each. The profit per unit is Rs 5. This perishable commodity he can keep in his shop for a week and at the end of each week the leftover are sold to a restaurant for Rs 3 each (at a loss of Rs 2 each). Mr John has given the record for the past 100 weeks for his weekly sales as given below:
Weekly demand 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Number of weeks 5 10 25 30 20 5 5
(i) Construct conditional profit table.
(ii) Find out the optimum number of units of this commodity to order weekly, so as to maximize his profit.
(iii) find out the Expected Profit of Perfect Information (EPPI).
(iv) find out the Expected Value of Perfect Information (EVPI).
(v) Interpret the value of EVPI.
(c) A businessman has two independent investments A and B available to him but he lacks capital to undertake both of them simultaneously. He can select to take A first and then stop, or if A is successful then take B, or vice versa. Probability of success for A is 0. 65 while for B it is 0.45. Both investments require an initial capital outlay of Rs 2,500.; and both return, nothing if venture is unsuccessful. Successful completion of A will return Rs 3, 500 (over cost) and successful completion of B will return Rs 5500 (over cost). Draw and estimate the decision tree by the roll back technique and find out the best strategy.