What happens to the indifference curves when a household's income is reduced?
Question
What is a budget constraint? How does a budget constraint explain consumer choices when used in conjunction with indifference curves? Explain what happens if a household looses half of their income, using a budget constraint and indifference curves in your discussion.
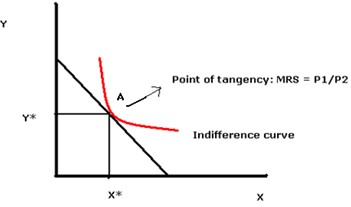
Budget constraint is defined as the locus of different combinations of goods that a consumer could consume/purchase given prices of goods and his income. A rational consumer maximizes his utility within his budget constraint. The utility of the consumer is represented by his indifference curve where Indifference curve is defined as the locus of different combination of goods from which the consumer gets the same level of satisfaction. So a rational consumer would be maximizing his utility where his indifference curve is tangent on budget constraint. At the point of tangency, their respective slopes would be equal and this situation is called first order condition for utility maximization. The slope of the budget constraint is price ratio -(p1/p2) and represent the rate at which the consumer can substitute one good for the other whereas the slope of the indifference curve is negative of Marginal rate of substitution (i.e. -MRS) and represent the rate at which consumer is willing to substitute one good for the other. It is only when these two rates are equal that the consumer would in equilibrium. So tangency between indifference curve and budget constraint would determine the optimal bundle for the consumer. As seen from the figure1 below, indifference curve and budget constraint are tangent at point A.
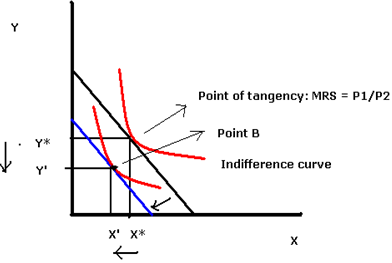
If a household loses half of this income, then budget constraint would shift inward parallel [from BC1 to BC2] implying now household can consume fewer amounts of both the goods. There would be only income effect. Assuming both the goods are normal, with this decreased income, the consumer would consume less of both the goods implying by new tangency point B.