1. Given the following information on the Chinese balance of payments (in billions of U.S. dollars), answer the questions below:
Exports of manufactured goods 100
Imports of machinery and equipment 80
Revenue from foreign tourists in China 10
Payments for foreign shipping services 15
Interest payments on foreign debt (net outflow) 5
Net borrowing from foreign lenders (bond sales) 10
Direct Foreign Investment (net inflow) 15
Deposits by Chinese nationals in foreign banks (net increase) 10
a. Show where each item goes in China's balance of payments [current account (CA) or financial account (FA); credit + or debit -], and calculate the CA and FA balances.
b. Assuming that there are no errors & omissions (no statistical discrepancy), and that the above information covers all non-official transactions, what must be the official reserve transactions (ORT) balance of China? How do you know?
c. What kind of action, if any, must the central bank of China ("People's Bank of China") be undertaking in this situation? Explain.
2. Show how the following transactions are recorded in India's balance of payments, using double-entry bookkeeping, i.e., show the credit (+) and debit (-) for each transaction. Also show in which account (current or capital/financial) each credit and debit is counted. Record all transactions in U.S. dollars using these exchange rates:
$1 = ¥100; $2.00 = £1; $1 = INR50 (INR is the new symbol for the Indian rupee)
a. India receives foreign aid (a transfer) in the form of a $1 million grant for a development project. The $1 million is in the form of a check drawn on an American bank.
b. India imports ¥100 million of farm machinery from Japan, which is paid for through the extension of trade credit by (i.e., a loan from) the Japanese exporter.
c. The Indian government sells bonds worth INR100 million (Rupees) to British investors; the investors obtain the Rupees (INR) from an Indian commercial bank in exchange for an equivalent value of British pounds (£).
d. The Indian commercial bank sells the pounds(£) obtained in part iii to the Reserve Bank of India (India's central bank) in exchange for an equivalent value of rupees (INR).
After all of these transactions are completed, what are the net changes in India's: current account, financial account, "overall" balance of payments, and official reserve transactions?
3. Here are data on the macroeconomic accounts of three (make-pretend) countries, measured in billions of currency units:

Calculate the trade balance (E - Z) and the net inflow of foreign saving (SF) for each country. State whether each one has a trade surplus or deficit (or balanced trade), and whether it is a net lender or borrower internationally, and explain in words.
4. Consider the following model of a medium-size European country, which is in a deep recession (values are in billions of euros; a * indicates the equilibrium value of a variable):

Answer the following questions:
a. Solve for the equilibrium national income or GDP (Y*). HINT: Use the equilibrium condition, E - Z = SH + SG - I, substitute the above numbers or functions, and solve for Y.
b. Solve for the equilibrium trade balance, (E-Z)*. State whether it is a surplus, balanced, or a deficit. HINT: Use your solution for equilibrium Y* to solve for equilibrium imports!
c. Solve for the equilibrium budget balance SG* (recall that SG = T - G is the government budget balance or "government saving"). State whether it is a surplus, balanced, or a deficit. HINT: Use your solution for equilibrium Y* to solve for equilibrium tax revenue!
d. Graph the solution on a diagram with income Y on the horizontal axis and the trade balance (E - Z) on the vertical axis, similar to the graph in #5 below (including the SH + SG - I and E - Z lines). Be sure to label all axes, lines, and points carefully, and indicate the precise slopes, intercepts, and equilibrium values (with exact numbers).
e. Due to austerity policies, government spending G is cut (reduced) by 100. How does this affect equilibrium national income (Y) and the trade balance (E-Z)? Calculate, show on a diagram, and explain briefly. Why does the trade balance change in the way that it does?
HINT: Solve for the change in Y first and then figure out how this affects E - Z.
f. The country successfully promotes its exports of olive oil, and exports E rise by 100.
How does this affect equilibrium national income (Y) and the trade balance (E - Z)?
HINT: Start your analysis from the original equilibrium from parts a.-d., and note that there are now two sources of change in E - Z in the new equilibrium!
5. The diagram below represents the U.S. economy, where there is substantial unemployment and a trade deficit. Using a series of diagrams of this type, analyze (separately) the effects of each of the following on both national income (Y) and the equilibrium trade balance (E - Z)
[show which line shifts and in which direction, and also show the changes in the equilibrium levels of Y and E-Z; qualitative answers (up/down, increase/decrease) are sufficient, but be sure to show the shifts on diagrams and explain briefly]:
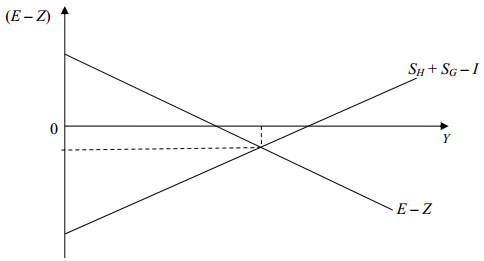
a. The government adopts a tax increase and cuts spending to reduce the budget deficit.
b. The government adopts a "fiscal stimulus" by increasing its spending on infrastructure.
c. Consumers borrow less and increase their saving rate as they struggle to get out of debt.
d. The dollar falls in value, making U.S. goods more competitive internationally.
e. As a result of increased outsourcing by U.S. corporations, imports increase.
f. As a result of a trade agreement that opens up a foreign market, exports increase.