Question 1) Determine whether the datasets below violate WARP and GARP.
Question 2) Consider a consumer that decides how much of n goods to consume while being taxed by the government. The government uses taxes over consumption, so that the expenditure in good i from consuming xi is
(pi + Τi) xi,
where Τi ∈ (0, 1) is the tax rate of good i. So the consumer effective prices (pi + Τi) for goods i. The consumer has total income y > 0. Suppose the consumer decides to consume x0 = (x01, . . . , x0n).
The government, however, decides to reform the tax system in order to only charge lump-sum taxes T ≥ 0. For the sake of fairness the lump-sum tax is set to that the tax revenue after the reform is equal to the pre-reform taxes
T ≡ i=1∑nΤix0i.
The pre-tax prices are unchanged by the reform. Suppose the post-reform consumption of the consumer is x1 (and assume x1 ≠ x2). Now consider the dataset containing the pre and post-reform effective prices and consumption levels.
a) Is either x0 or x1 revealed to be preferred to each other? Explain.
b) Suppose the consumer has locally non-satiated preferences. Can we say in which regime the consumer is better off? Weakly or strictly?
c) Now suppose that, initially, only good 1 was taxed (Τi = 0 for i = 2, . . . , n). If the dataset satisfies WARP, can we say what happens to the consumption of good 1 as a result of the reform?
Question 3) Suppose the consumer has Bernoulli utility over monetary amounts u(·) satisfying
u (x) = ax + bx2.
a) Can you express the expected utility of this consumer for any probability distribution F as a linear combination of the mean and variance of distribution F?
Question 4) For a given utility over monetary amounts u (·) we define the measure of relative risk aversion as
rr (x) = - (u''(x)/u'(x))x.
a) Show that the only utility function satisfying
rr (x) = ρ, for all x,
for ρ > 0 with ρ ≠ 1 is the function (or an affine transformation of)
u (x) = x1-ρ/1- ρ,
which is called the constant relative risk aversion utility (CRRA).
b) Consider a consumer with expected utility over monetary amounts given by the CRRA utility above with parameter ρ. This consumer has initial money W > 0 and faces the risk of a loss. A loss occurs with probability α ∈ (0, 1) and is a monetary loss of L ∈ (0, W). Write down the expected utility of this consumer.
c) Now suppose this consumer can purchase insurance. The cost per overage is p ∈ (0, 1).
An insurance policy with coverage c ≥ 0 costs pc, which is paid regardless of whether there is a loss or not. In case of a loss, the consumer receives payment equal to the coverage c > 0. Write down U (c), the expected utility of this consumer in case he has coverage c.
d) Given price per coverage p > 0, find the optimal level of coverage for the consumer (you can assume it's strictly positive). How does it depend on α, p and ρ?
e) What happens if p = α?
f) Determine the price level for which the consumer would buy zero coverage.
Question 5) For a given utility over monetary amounts u (·) we define the measure of absolute risk aversion (or Arrow-Pratt measure) as
rA (x) = u''(x)/u'(x).
a) Show that the only utility function satisfying
rA (x) = ρ, for all x,
for ρ > 0 is the function (or an affine transformation of)
u (x) = - (1/ρ)e-px,
which is called the absolute relative risk aversion utility (CARA). Redo steps (a)-(f) with this utility.
Question 6) Consider a set of outcomes A = (a1, a2, a3) and two possible Bernoulli utility functions
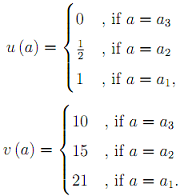
a) The two induced expected utility represent the same preferences over gambles involving {a1, a2, a3}? If not, then construct two simple gambles for which the preference ordering under u (·) and v (·) are reversed.
b) Can we substitute v (a1) by any specific number so that the answer to item a would change?
Question 7) Consider the production function f (x1, x2) = min {ln (x1), x2}.
a) Draw the isoquants of f(·).
b) Find the conditional input demands.
c) Find the cost function.
d) Find the output supply function.
e) Find the profit function.
f) Find the unconditional input demands.
Question 8) Consider the production function f (x1, x2) = log (√x1 + √x2).
a) Find the conditional input demands.
b) Find the cost function.
c) Find the output supply function.
d) Find the profit function.
e) Find the unconditional input demands.