Part -1:
1: List three barriers to entry and explain how each can help create market power
1. (Barriers to Entry) Explain how economies of scale can be a barrier to entry.
2. (Barriers to Entry) Identify the other two barriers to entry and explain how they block new firms from this market.
2: Distinguish marginal revenue and average revenue for a monopolist, and explain why marginal revenue is less than average revenue
3. (Monopoly) Suppose that a certain manufacturer has a monopoly on the sorority and fraternity ring business (a constant-cost industry) because it has persuaded the "Greeks" to give it exclusive rights to their insignia.
a, Using demand and cost curves, draw a diagram depicting the firm's profit-maximizing price and output level.
b. Why is marginal revenue less than price for this firm?
c. On your diagram, show the deadweight loss that occurs because the output level is determined by a monopoly rather than by a competitive market.
d. What would happen to price and output if the Greeks decided to charge the manufacturer a royalty fee of $3 per ring?
3: Determine the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing production level for a monopolist
4. (Short-Run Profit Maximization)Answer the following questions on the basis of the monopolist's situation illustrated in the following graph.
a. At what output rate and price does the monopolist operate?
b. In equilibrium, approximately what is the firm's total cost and total revenue?
c. What is the firm's economic profit or loss in equilibrium?
4: Summarize what causes the deadweight loss of monopoly
5. (Monopoly and the Allocation of Resources) What is the problem with monopoly? Compare monopoly to the benchmark of perfect competition established in the previous chapter. Use the exhibit below for reference. Identify the deadweight loss.
5: Outline the factors that could cause the deadweight loss of monopoly to be lower or higher than expected
6. (Allocative and Distributive Effects) Why is society worse of under monopoly than under perfect competition, even if both market structures face the same constant long-run average cost curve?
7. (Welfare Cost of Monopoly) Explain why the welfare loss of a mo¬nopoly may be smaller or larger than the loss shown in the exhibit above.
6: Explain why a firm with market power might decide to charge different groups different prices.
8. (Conditions for Price Discrimination) List three conditions that must be met for a monopolist to price discriminate successfully.
9. (Price Discrimination) Explain how it may be profitable for South Korean manufacturers to sell new autos at a lower price in the United States than in South Korea, even with transportation costs included.
10. (Perfect Price Discrimination) Why is the perfectly discriminating monopolist's marginal revenue curve identical to the demand curve it faces?
Part -2:
1. Outline the monopolistic and competitive elements of monopolistic
1. (Short-Run Profit Maximization) A monopolistically competitive firm faces the following demand and cost structure in the short run:
| Output |
Price |
FC |
VC |
TC |
TR |
Profit/Loss |
| 0 |
$100 |
$100 |
$0 |
__ |
__ |
__ |
| 1 |
90 |
__ |
50 |
__ |
__ |
__ |
| 2 |
80 |
__ |
90 |
__ |
__ |
__ |
| 3 |
70 |
__ |
150 |
__ |
__ |
__ |
| 4 |
60 |
__ |
230 |
__ |
__ |
__ |
| 5 |
50 |
__ |
330 |
__ |
__ |
__ |
| 6 |
40 |
__ |
450 |
__ |
__ |
__ |
| 7 |
30 |
__ |
590 |
__ |
__ |
__ |
a. Complete the table.
b. What is the highest profit or lowest loss available to this firm?
c. Should this firm operate or shut down in the short run? Why?
d. What is the relationship between marginal revenue and mar-ginal cost as the firm increases output?
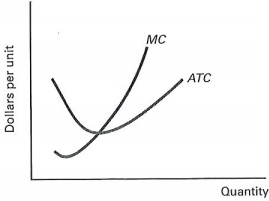
2. (Monopolistic Competition and Perfect Competition Compared) Illustrated below are the marginal cost and average total cost curves for a small firm that is in long-run equilibrium.
a. Locate the long-run equilibrium price and quantity if the firm is perfectly competitive.
b. Label the price and quantity pi and q1.
c. Draw in a demand and marginal revenue curve to illustrate long-run equilibrium if the firm is monopolistically competitive. Label the price and quantity p2 and q2.
d. How do the monopolistically competitive firm's price and output compare to those of the perfectly competitive firm?
e. How do long-run profits compare for the two types of firms?
3. (Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition) Why is a firm in monopolistic competition said to be competitive? In what sense is that firm monopolistic?
2- Describe the sources of oligopoly and explain why some industries become oligopolies
4. (Oligopoly Power) What are three sources of oligopolies?
5. (Varieties of Oligopolies) Do the firms in an oligopoly act independently or interdependently? Explain your answer.
3 - Explain why predicting oligopoly behavior is so difficult
6. (Price Leadership) Why might a price-leadership model of oligopoly not be an effective means of collusion in an oligopoly?
7. (Collusion and Cartels) Why would each of the following induce some members of OPEC to cheat on their cartel agreement?
a. Newly joined cartel members are less-developed countries.
b. The number of cartel members doubles from 12 to 24.
c. International debts of some members grow.
d. Expectations grow that some members will cheat.
8. (Collusion and Cartels) Use revenue and cost curves to illustrate and explain the sense in which a cartel behaves like a monopolist.
9. (Game Theory) Suppose there are only two automobile companies, Ford and Chevrolet. Ford believes that Chevrolet will match any price it sets, but Chevrolet too is interested in maximizing profit. Use the following price and profit data to answer the following questions.
| Ford's Selling |
Chevrolet's |
Ford's |
Chevrolet's |
| Price |
Selling |
Profits |
Profits |
|
Price |
(millions) |
(millions) |
| $4,000 |
$4,000 |
$8 |
$8 |
| 4,000 |
8,000 |
12 |
6 |
| 4,000 |
12,000 |
14 |
2 |
| 8,000 |
4,000 |
6 |
12 |
| 8,000 |
8,000 |
10 |
10 |
| 8,000 |
12,000 |
12 |
6 |
| 12,000 |
4,000 |
2 |
14 |
| 12,000 |
8,000 |
6 |
12 |
| 12,000 |
12,000 |
7 |
7 |
a. What price will Ford charge?
b. What price will Chevrolet charge once Ford has set its price?
c. What is Ford's profit after Chevrolet's response?
d. If the two firms collaborated to maximize joint profits, what prices would they set?
e. Given your answer to part (d), how could undetected cheating on price cause the cheating firm's profit to rise?
10. (Game Theory) While grading a final exam, an economics profes¬sor discovers that two students have virtually identical answers. She is convinced the two cheated but cannot prove it. The profes¬sor speaks with each student separately and offers the following deal: Sign a statement admitting to cheating. If both students sign the statement, each will receive an "F" for the course. If only one signs, he is allowed to withdraw from the course while the other student is expelled. If neither signs, both receive a "C" because the professor does not have sufficient evidence to prove cheating.
a. Draw the payoff matrix.
b. Which outcome do you expect? Why?
11. (Oligopoly Behavior) Why is firm behavior under oligopoly so difficult to predict?