Multiple Choice problems
Instructions: Enter either A, B, C, or D (only one) after each of the following problems to indicate your best answer.
problem1)
Taxes and permits provide incentives for firms to:
A. Invest in new, more cost-effective abatement technologies
B. Achieve economic efficiency.
C. Provide regulatory agencies information on abatement costs.
D. A and B
problem2)
Which of the following can be used to correct for externalities in large numbers cases:
A. Taxes
B. Directives
C. All of the above.
D. None of the above.
problem3)
Uniform directive polices penalize:
A. Firms with high abatement costs.
B. Firms with low abatement costs.
C. Firms that do not have equal abatement costs.
D. Firms that have equal abatement costs.
problem4)
There is a higher incidence of pollution taxes on producers if:
A. Pollution taxes are imposed equi-marginally.
B. The pollution is associated with the production of luxuries.
C. There is a market failure.
D. The pollution is associated with the production of necessities.
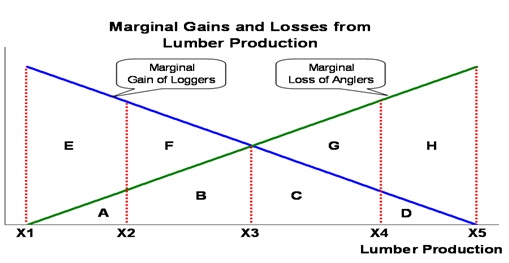
The figure given above describes the costs and benefits resulting from logging operations in a national forest. A logging company gains profits from increased lumber production according to the "Marginal Gain of Loggers" curve. At the same time, recreational anglers lose fishing opportunities in trout streams that are negatively affected by the logging operations. The "Marginal Loss of Anglers" curve describes the loss of value suffered by these anglers as lumber production increases. The letters A through H describe individual areas within the graph.
For problems 5 through 8, assume that the Forest Service has decided to allow the logging company to harvest any amount of lumber from X1 to X5. Further assume that the anglers are not organized enough to be able to affect that decision.
problem5)
What level of lumber production will result without negotiation?
A. X1
B. X3
C. X5
D. None of the above.
problem6)
What will be the total loss suffered by the anglers without negotiation?
A. Areas A + B + C + D + E + F
B. Areas A + B + E + F
C. Areas C + D + G + H
D. Areas A + B + C + D + G + H
problem7)
What would be the total potential gains from trade if the logging company and the anglers were able to negotiate?
A. Areas A + B
B. Areas E + F
C. Areas C + D
D. Areas G + H
problem8)
If the logging company was considering an offer of compensation by the anglers for a reduction in production from X5 to X4, what would be its minimum willingness to accept payment?
A. Area A
B. Areas A + B
C. Areas C + D
D. Area D
problem9)
The fundamental principle of the Porter Hypothesis is:
A. Different efficient allocations can be achieved by market processes through appropriate re- distributions of wealth.
B. Environmental regulations must be both stringent enough and flexible enough to induce firms to meaningfully re-examine their production processes
C. The total amount of mass and energy is constant (although mass and energy can interconvert).
D. Given an initial allocation the (perfectly competitive) market achieves an efficient allocation.
problem10)
Net benefit is the appropriate measure of desirability since:
A. Cost must be added to the benefits to determine the desirability of the action.
B. It reflects the reality that costs must be paid.
C. It achieve economic efficiency.
D. A and C
problem11)
The marginal benefits of abatement generally decrease as the level of abatement increases because:
A. An increase in abatement given an already high level of abatement is generally valued less than a similar increase given a low level of abatement.
B. An increase in abatement given an already high level of abatement generally costs more than a similar increase given a low level of abatement.
C. The marginal benefit curve needs to cross the marginal cost curve to achieve economic efficiency.
D. The marginal benefit curve is also known as a demand curve and demand curves slope downward.
problem12)
An economic allocation describes:
A. A potential distribution of wealth (or resources).
B. Is not necessarily fair.
C. Requires someone to be rich and someone to be poor.
D. A and B
problem13)
Externalities violate which characteristic of efficient property rights
A. Exclusivity
B. Universality
C. Transferability
D. Enforceability
problem14)
Which of the following is not an impediment to economic efficiency
A. Externalities.
B. Property resources that are not exclusively controlled by an individual.
C. The initial distribution of resources or wealth.
D. Public goods.
problem15)
Which of the following does not tend to cause a "free rider" problem.
A. One cannot exclude use by others.
B. Governments achieve distributive equity.
C. Benefits are simultaneously provided to many individuals
D. A, B, and C