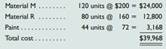
Question: If the working papers that accompany this book are unavailable, do not attempt to solve this problem. Sagrillo Company manufactures variations of its product, a technopress, in response to custom orders from its customers. On May 1, the company had no inventories of goods in process or finished goods but held the following raw materials.
On May 4, the company began working on two technopresses: Job 102 for Global Company and Job 103 for Rolf Company.
Required Follow the instructions in this list of activities and complete the sheets provided in the working papers.
a. Purchased raw materials on credit and recorded the following information from receiving reports and invoices.
Receiving Report No. 426, Material M, 150 units at $200 each.
Receiving Report No. 427, Material R, 70 units at $160 each.
Instructions: Record these purchases with a single journal entry and post it to general ledger T-accounts, using the transaction letter a to identify the entry. Enter the receiving report information on the materials ledger cards.
b. Requisitioned the following raw materials for production.
Requisition No. 35, for Job 102, 80 units of Material M.
Requisition No. 36, for Job 102, 60 units of Material R.
Requisition No. 37, for Job 103, 40 units of Material M.
Requisition No. 38, for Job 103, 30 units of Material R.
Requisition No. 39, for 12 units of paint.
Instructions: Enter amounts for direct materials requisitions on the materials ledger cards and the job cost sheets. Enter the indirect material amount on the materials ledger card and record a debit to the Indirect Materials account in the subsidiary factory overhead ledger. Do not record a journal entry at this time.
c. Received the following employee time tickets for work in May
Time tickets Nos. 1 to 10 for direct labor on Job 102, $40,000.
Time tickets Nos. 11 to 30 for direct labor on Job 103, $32,000.
Time tickets Nos. 31 to 36 for equipment repairs, $12,000.
Instructions: Record direct labor from the time tickets on the job cost sheets and then debit indirect labor to the Indirect Labor account in the subsidiary factory overhead ledger. Do not record a journal entry at this time.
d. Paid cash for the following items during the month: factory payroll, $84,000, and miscellaneous overhead items, $36,000. Instructions: Record these payments with journal entries and then post them to the general ledger accounts. Also record a debit in the Miscellaneous Overhead account in the subsidiary factory overhead ledger.
e. Finished Job 102 and transferred it to the warehouse. The company assigns overhead to each job with a predetermined overhead rate equal to 70% of direct labor cost. Instructions: Enter the allocated overhead on the cost sheet for Job 102, fill in the cost summary section of the cost sheet, and then mark the cost sheet "Finished." Prepare a journal entry to record the job's completion and its transfer to Finished Goods and then post it to the general ledger accounts.
f. Delivered Job 102 and accepted the customer's promise to pay $290,000 within 30 days. Instructions: Prepare journal entries to record the sale of Job 102 and the cost of goods sold. Post them to the general ledger accounts.
g. Applied overhead to Job 103 based on the job's direct labor to date. Instructions: Enter overhead on the job cost sheet but do not make a journal entry at this time.
h. Recorded the total direct and indirect materials costs as reported on all the requisitions for the month. Instructions: Prepare a journal entry to record these costs and post it to general ledger accounts.
i. Recorded the total direct and indirect labor costs as reported on all time tickets for the month. Instructions: Prepare a journal entry to record these costs and post it to general ledger accounts.
j. Recorded the total overhead costs applied to jobs. Instructions: Prepare a journal entry to record the allocation of these overhead costs and post it to general ledger accounts.