|
Products
|
W1
|
W2
|
W3
|
W4
|
W5
|
W6
|
W7
|
W8
|
W9
|
|
P1
|
100
|
200
|
150
|
150
|
50
|
300
|
200
|
250
|
000
|
|
P2
|
200
|
100
|
150
|
350
|
50
|
100
|
150
|
250
|
500
|
|
P3
|
200
|
250
|
200
|
000
|
400
|
100
|
150
|
000
|
000
|
|
Total
|
500
|
550
|
500
|
500
|
500
|
500
|
500
|
500
|
500
|
Table 1. 9 weeks Master Production Scheduling for 3 products
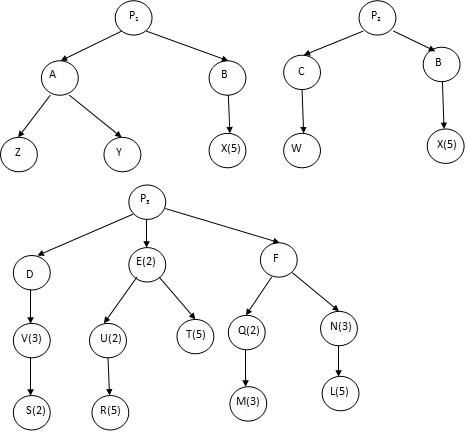
Figure 1. Bill of Materials for three products
|
Parts
|
P1
|
Unit Price of Material
|
P2
|
Unit Price of Material
|
P3
|
Unit Price of Material
|
|
A
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
|
B
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
|
C
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
|
D
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
|
E
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
|
F
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
--
|
|
|
L
|
|
|
|
|
5
|
15
|
|
M
|
|
|
|
|
8
|
20
|
|
N
|
|
|
|
|
12
|
15
|
|
Q
|
|
|
|
|
15
|
30
|
|
R
|
|
|
|
|
7
|
20
|
|
S
|
|
|
|
|
10
|
20
|
|
T
|
|
|
|
|
8
|
40
|
|
U
|
|
|
|
|
15
|
20
|
|
V
|
|
|
|
|
10
|
50
|
|
W
|
|
|
15
|
40
|
-
|
|
|
X
|
25
|
25
|
20
|
25
|
-
|
|
|
Y
|
15
|
30
|
-
|
|
-
|
|
|
Z
|
10
|
30
|
-
|
|
-
|
|
Table 2. The amount of materials used in production for each part as KG and the price of the related material as Turkish Lira.
|
Parts
|
Standard Time for each Unit Operation
|
Machine Used for the Operations
|
|
A
|
10
|
-
|
|
B
|
5
|
-
|
|
C
|
5
|
-
|
|
D
|
8
|
-
|
|
E
|
10
|
-
|
|
F
|
12
|
-
|
|
L
|
12
|
M3
|
|
M
|
15
|
M1
|
|
N
|
15
|
M3
|
|
Q
|
10
|
M2
|
|
R
|
15
|
M2
|
|
S
|
10
|
M1
|
|
T
|
15
|
M2
|
|
U
|
12
|
M1
|
|
V
|
14
|
M3
|
|
W
|
9
|
M1
|
|
X
|
11
|
M3
|
|
Y
|
14
|
M1
|
|
Z
|
8
|
M3
|
Table 3. Unit stadard operation times for the parts at machines as minutes
|
Products
|
P1
|
P2
|
P3
|
|
Standard Time for Assembly Operations (min.)
|
30
|
25
|
45
|
|
# operators
|
2
|
2
|
3
|
|
Cost of each operator (TL/h)
|
75
|
75
|
75
|
Table 4. Standard times and the cost of the operators for the final assembly operations for three products
Manufacturing system uses a mixture of automated and manual material handling system and for this purpose employs two forklifts and a partially run automated guided vehicle (AGV) within the system. Operating cost of a forklift is 200 TL/h including operator cost and operation cost of AGV is 100TL/h. On average, forklift is used 5h/shift and AGV is used 4h/shift. Further, transferring a batch of part to and from a machine to and from any destination takes 15 minutes on average including waitings.
The purchase costs of CNC machines are 90,000TL, 120,000 TL, and 150,000 TL respectively. The economic lives of the machines are standart 12 years for all the machines. The purchase cost of each forklift is 30,000TL and the economic life of a forklift is 6 years. The cost of AGV is 500,000TL and the economic life of the system is 20 years. The maintanance costs of the machines 2500 TL/each/year; of the forklift is 1500 TL/each/year; and of the AGV system is 10,000 TL/year.
Batch of parts, time to time, depends on the machine or equipment availability, may wait to be assigned to their destinations and on average, every batch waits in system 60 minutes. As a company policy, the batch sizes are arranged as 10 components.
Although machines are automated an operator is assigned to each machine during the entire shift and they are responsiple for seting up machines, loading and unloading parts, cleaning machine tables, exchanging the worn or broken tools, and doing minor additional operations and cost of each operator is 100TL/h.
Company further employs 10 more workers to do several utility and direct work such as setting up batches, assembly stations, running warehouse, tool management, maintanance, etc. Cost of each worker is, on average 60TL/h.
Company employs some office staff as well for different purposes, such as accounting, marketing, sales, purchasing, part programming, process planning, and administration and cost of each staff is 80TL/h on average and the number of people employed is 10.
Machines work constantly during the normal working shifts and maintanance is done outside of working hours. The average utilization of machines is 90%, and the efficiency of the machines is 110%.
All the rest of expenditures, such as electricity, water, gas, communication, catering, security, and some clerical jobs are collected under the overhead costing category and the total expenditure made during 9 weeks periods is 125,000 TL.
Q.1. Calculate the cost of each product and total cost of manufacturing using standard costing system.
Q.2. Calculate the cost of each product and total cost of the manufacturing using Traditional Costing System.
Note. Exam paper is due on 29 November 2016 at the lecture hours.