Managerial Economics Assignment
Question 1 -
(a) You are taking two courses this semester: Economics and Mathematics. You have two examinations coming up in both classes. The table below shows your grade on each examination for different numbers of hours spent studying for each course:
|
Hours of Study
|
Economics
|
Mathematics
|
|
0
|
70
|
60
|
|
1
|
77
|
68
|
|
2
|
82
|
74
|
|
3
|
85
|
78
|
Your goal is to maximise your average grade on the two examinations. Use the benefit cost analysis to decide how much time you would spend studying for each examination if you had three hours in total to prepare for the two examinations. Note: you can only choose to study in increments of one hour. In your analysis, identify the appropriate marginal costs and benefits, and explain how the economic concept of decision making on the margin is used to solve the problem.
(b) When Steven graduated from university and got a job, his income rose from $15,000 to $60,000. His consumption habits also changed drastically. For instant noodles, his consumption falls from 7 packs a week to zero. For movies, his consumption rises from 1 per year to 11 per year.
(i) Calculate his income elasticity of demand for both instant noodles and movies using the midpoint formula.
(ii) Explain how you would classify the two goods, instant noodles and movies, based on the income elasticity of demand.
(iii) Define what the income elasticity of demand measures. If more consumption is generally preferred to less consumption, why do some goods have negative income elasticities?
(iv) If the economy enters a recession, how would this affect the revenues of the seller of instant noodles and the movie theatre operator? Explain.
Question 2 -
(a) You have decided to spend $40 this month on Fish and Bread. The total utility you receive from different quantities of fish and bread are shown in the table below. The prices of fish and bread are both $10 per unit.
|
Quantity
|
Total Utility of Fish
|
Total Utility of Bread
|
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
200
|
140
|
|
2
|
360
|
260
|
|
3
|
500
|
360
|
|
4
|
620
|
440
|
Apply the rational spending rule to determine the combination of Fish and Bread that optimises your total utility. Explain why applying the rational spending rule is a more appropriate decision making tool for optimizing consumption, compared to simply evaluating the total utility of different bundles of goods.
(b) A large pharmaceutical company estimates that the demand function for its medicine is P = 60 - 5Q. It is currently selling the medicine at $40 per unit.
(i) Calculate the price elasticity of demand at this price.
(ii) Do you think it is a good idea for the company to raise its price to earn more revenue? Explain your answer using the relevant elasticity concepts without reference to graphs or equations.
(iii) At what price does the company maximise its revenue? Show your work.
Question 3 -
The following graph shows the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
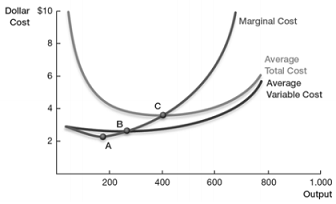
(a) If the market price is $6, comment on the profit or loss incurred by the firm. Explain whether the firm will operate or shut down in the short run.
(b) If the market price is $3, comment on the profit or loss incurred by the firm. Explain whether the firm will operate or shut down in the short run.
(c) If the market price is $1, comment on the profit or loss incurred by the firm. Explain whether the firm will operate or shut down in the short run.
(d) Consider the three points, A, B, and C marked on the graph. Discuss the characteristics of these three points. Which point represents the long run equilibrium of the firm?
Question 4 -
Consider a monopolist producer who faces a linear demand curve P = 24 - Q, where P is the price the producer charges and Q is the quantity consumers purchase. The producer produces this good at a constant average and marginal cost of $6.
(a) Identify the price and quantity if the monopolist wishes to maximise revenue.
(b) Identify the price and quantity if the monopolist wishes to maximise profits. Support your answer with a diagram.
(c) Suppose the government imposes a tax of T dollars per unit on the producer. By how much will the consumer shoulder the tax burden? By how much will the producer shoulder the tax burden? Explain why, in general, the consumer shoulders part of a tax burden even when the tax is imposed directly on the producer.