MACROECONOMICS ASSIGNMENT
1. Macroeconomists tend to focus on three major price categories which include:
a. Consumer prices, interest rates, and exchange rates
b. Consumer prices, Producer prices, and Government prices
c. Consumer prices consisting of: Normal Good prices, Inferior Good prices, & Luxury Good prices
d. Consumer prices consisting of: Oil prices, Food prices, and Energy prices
2. When studying inflation regarding consumer goods, what is the disadvantage of using CPI?
a. CPI includes several goods the consumer is uninterested in
b. The CPI basket changes monthly making comparisons over time difficult
c. The CPI basket is fixed and thus ignores the consumer's ability to substitute away from more expensive goods
d. CPI excludes imported goods
3. When studying inflation regarding consumer goods, what is the disadvantage of using GDP deflator?
a. GDP deflator uses a fixed basket of goods
b. GDP deflator includes several goods which are unimportant to the typical consumer
c. GDP deflator includes imported goods
d. GDP deflator excludes exported goods
4. When inflation rises:
a. the nominal interest rate will rise
b. the real interest rate will rise
c. real GDP increases
d. real GDP decreases
5. When the Bank of Canada pursues expansionary monetary policy:
a. increased demand for Canadian currency will cause the Canadian dollar to increase in value
b. increased demand for Canadian currency will cause the Canadian dollar to fall in value
c. increased supply of Canadian currency will cause the Canadian dollar to fall in value
d. increased supply of Canadian currency will cause the Canadian dollar to increase in value
6. A high interest rate:
a. makes borrowing funds cheaper
b. tends to increase the money supply
c. decreases the opportunity cost of holding money in cash form
d. increases the opportunity cost of holding money in cash form
7. The real interest rate consists of:
a. the cost of borrowing
b. the cost of borrowing + inflation
c. the cost of borrowing + risk + inflation
d. the cost of borrowing + risk
8. Say the world price of oil increases. Note that Canada exports oil to several countries. Based on the supply and demand for Canadian currency, what will happen to the value of the Canadian dollar?
a. The increase in oil prices is unrelated to currency values; therefore, no change will occur
b. Countries will need to purchase more Canadian money which will decrease the value of the currency
c. Canada will supply less oil because of the price increase which will cause the value of their currency to fall
d. Countries will need to purchase more Canadian money which will increase the value of the currency
9. In an effort to boost the economy, the Bank of Canada may consider:
a. increasing the money supply; increasing interest rates
b. decreasing the money supply; increasing interest rates
c. increasing the money supply; decreasing interest rates
d. decreasing the money supply; decreasing interest rates
10. When inventories in an economy accumulate, it is typically a sign that:
a. unplanned investment has increased and a potential economic slowdown looms
b. planned investment has increased and a potential economic slowdown looms
c. economic productivity has been decreasing
d. unplanned investment has increased suggesting future economic expansion
11. Which of the following best describes the multiplier effect?
a. Having a bird in the hand is worth two in the bush
b. Like sand through an hour glass
c. The spreading of ripples from a stone thrown in a pond
d. A rolling stone gathers no moss
12. It has been found that people tend to save less in an economy. What happens to the aggregate consumption function?
a. The slope gets steeper - i.e. MPC rises
b. The function shifts upward - i.e. MPC rises
c. The slope gets flatter - i.e. MPC falls
d. The function shifts downward - i.e. MPC falls
13. Which of the following is NOT a part of planned aggregate spending?
a. Consumption
b. Investment
c. government expenditures
d. Inventories
14. Suppose investment increases by $100 and, as a result, GDP ultimately increases by $200. What does the multiplier equal?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
15. Suppose the economy is currently at equilibrium at $1 trillion, and the MPC is 0.6. And suppose there is a $100 billion decrease in government purchases of goods and services. Which of the following is the new equilibrium?
a. $400 billion
b. $600 billion
c. $750 billion
d. $1.4 trillion
16. Suppose the marginal propensity to consume equals 0.9. What is the multiplier?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 5
d. 10
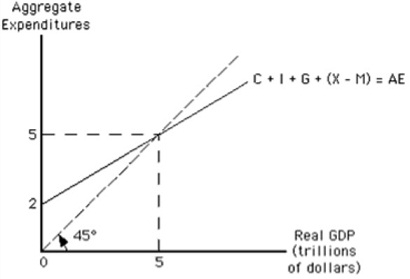
17. Refer to the graph in the exhibit. Assume the economy is in equilibrium with real GDP of $5 trillion. Suppose aggregate expenditure increases by $1 trillion. How would the economy's equilibrium real GDP most likely be affected?
a. It would increase by more than $1 trillion.
b. It would increase by $1 trillion.
c. It would increase by less than $1 trillion.
d. It would decrease by $1 trillion.
18. Other things constant, how would a smaller marginal propensity to save affect the multiplier?
a. The multiplier would increase.
b. The multiplier would remain the same.
c. The multiplier would become smaller.
d. The multiplier would be negative.
19. Suppose autonomous investment increases by $100 billion. How will the equilibrium real GDP demanded be affected?
a. It will increase by $100 billion.
b. It will increase by ($100 billion)/MPC.
c. It will increase by $100 billion × MPC.
d. It will increase by $100 billion/MPS.
20. Consider an economic model with no income taxes and no international trade. Suppose the marginal propensity to consume in Canada is 3/5, and the marginal propensity to save in India is 1/10. Which of the following characterizes how the Indian and Canadian economies would be affected?
a. Increases in government purchases would increase real GDP demanded more per dollar in India than in Canada.
b. Decreases in government purchases would increase real GDP demanded more per dollar in India than in Canada.
c. Increases in autonomous saving would increase real GDP demanded more per dollar in India than in Canada.
d. Real GDP demanded would be higher in India than in Canada.