Economics of Money and Banking Assignment -
Question 1 - Consider the following version of the model in chapter 6. There is no population growth. The number of young individuals born on island i in period t, Ni, is random according to the following specification:
Ni = 4/5 N with probability 0:5
= 1/5 N with probability 0:5
Assume that the fiat money stock grows at the fixed rate zt = z in all periods.
a) Set up the budget constraints of the individuals when young and when old in terms of lit. Also set up the government budget constraint and money market-clearing condition. Find the lifetime budget constraint (combine the budget constraints of the young and old by substituting for lit).
b) On which island would you prefer to be born? Explain with reference to the rate of return to labor.
c) Show how the rate of return to labor and the individual's labor supply depend on the value of z.
For the following parts, assume that the growth rate of the fiat money stock zt is random according to
zt = 1 with probability θ
= 4 with probability 1 - θ
The realization of zt is kept secret from the young until all purchases of goods have occurred (i.e., individuals do not learn Mt until period t is over). Given these changes in assumption, answer the following questions:
d) How many states of the world would agents be able to observe if information about every variable were perfectly available? Describe those possible states.
e) How many states of the world are the agents able to distinguish when there is limited information (i.e., they do not know the value of zt)?
f) Draw a graph of labor supply and the growth rate of the fiat money stock in each possible state of the world when there is limited information. What is the correlation observed between money creation and output?
g) Suppose the government wanted to take advantage of the relation between money creation and output. If it always inflates, will the graph you derived in part f remain the same? Explain fully.
Part B -
Question 1 - Individuals are endowed with y units of the consumption goods when young and nothing when old. Assume that people face a lump-sum tax of τ goods when old and a rate of expansion of the fiat money supply of z > 1 (that is, Mt = zMt-1). The tax and the expansion of the fiat money stock are used to finance government purchases of goods per young person in every period (gt). Let Gt represents total government purchases, i.e. Gt = Ntgt.
There are Nt people born in time t and gross rate of population growth is n.
a) Write down the feasible constraint. Rewrite it for stationary case.
b) Find the individual's budget constraints when young and when old. Combine them to form the individual's lifetime budget constraint.
c) Find the government's budget constraint.
d) Find the rate of returne on money.
e) Find the stationary monetary equilibrium when z = 1 and n = 1. Compare the stationary feasible set with the stationary lifetime budget constraint.
Question 2 - Let Nt = nNt-1 and Mt = zMt-1 for every period t, where z and n are both greater than 1. The money created each period is used to finance a lump-sum subsidy of ρ goods to each young person. The difference between this question and Question 1 is that a young receives lump-sum subsidy of and there is no direct tax. Hence, he first period budget constraint is
c1,t + vtmt = y + ρ (1)
The budget constraint of an old person
c2,t+1 = vt+1mt
Hence the lifetime budget constraint obtain by finding mt from the second period budget constraint and substitute that into the first period budget constraint.
c1,t + (vt/vt+1)c2,t+1 = y + ρ
Similar to Question 1 the rate of return on money is obtained from market clearing condition. The money market-clearing conditions is given by total money demand is equal to total money supply. That is vtMt = Nt(y-c1,t). Hence,
vt = Nt(y-c1)/Mt (2)
The rate of return of fiat money (under a population growth n and no change in endowment).
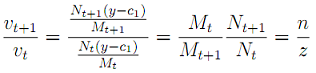
a) What is the government budget constraint? Use the market clearing condition for money and find ρ.
b) Rewrite the life time budget constraint by substituting the rate of returne of money and ρ. Impose the stationary equilibrium.