Assignment
SECTION OVERVIEW: This last microeconomic section presents "advanced topics in managerial economics." We analyze how firms may make alternative pricing decisions to our standard single-price, MR=MC rule. Chapter 14 examines pricing under market segmentation and when the firm produces multiple products. Chapter 16 examines the impact that government regulation can have on business, usually to counteract situations where firms exercise market power or where market failures exist.
LEARNING GOALS: Upon completing this section, we will understand the various forms of price discrimination and when they may allow a firm to reap more profit than uniform pricing. We will also analyze pricing decisions for firms that produce products related in consumption in contrast to single-product production or firms producing multiple but unrelated products. We will understand how markets may or may not exhibit efficiency, and how government intervention can correct market failure.
1. The following shows the demands and marginal revenue in two markets, 1 and 2, for a price discriminating firm along with total marginal revenue, MRT, and marginal costMC.
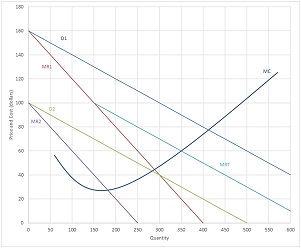
For reference, P1 = 160 - 0.2Q and P2 = 100 - 0.2Q.
a. Compare the demand conditions in each market; i.e. how do the two markets differ in their demand for the firm's product?
b. How much total output should the firm produce (for both markets combined)? How should that output be allocated between markets 1 and 2? (It would be easiest to copy and paste the picture above and draw directly on the picture using Insert, Shapes to do parts b and c.)
c. What price should the firm charge in each market?
2. On Amazon.com, there are three versions of Keynes' famous General Theory: a hardcover for $28.65, paperback for $11.99, and a Kindle version for $1.00. There is not much difference in the cost of production between hardcover and paperback books (though there likely is for the Kindle e-book version), but hardcover books do tend to be published earlier than paperback versions of the same book. How do you explain the wide variety of prices for basically the same book?
3. Shaughnessy Consulting, LLC currently enjoys a patent on software that estimates economic damages for clients involved in personal injury lawsuits. Demand for my softwareis
QD = 80 - 2P. Creating the software cost me about $2,000 in development and coding.I can produce a copy of the software for $2 per unit (constant cost).
a. How many copies of the software should I attempt to sell? At what price should I sell it? How much profit would I make?
b. My patent expires in a year, and I know other economic consultants will produce competing software. What quantity and price will result once competing software emerges? How much consumer surplus will my clients (lawyers) gain once the competitors enter?(For measuring consumer surplus, recall that area of a triangle = ½ * base * height.)
c. How much deadweight loss is created by my patent and monopoly in this software?
4. After considering the situation of market power for my software and how it changed after the introduction of competitors, consider situations of natural disasters and how governments respond to shortages resulting from them.
a. Read this article "We Can't Stop the Twisters, But We Can Stop Price Gouging" by Sonya Ziaja and comment on why anti-gouging laws can increase social welfare.
b. In contrast, read the blog post "Gouging Reality" by Don Boudreaux and comment on why anti-gouging laws may not increase social welfare, or at least why they may lead to consequences which are unintended by the government.
c. Which argument do you find more persuasive, and why? I.e., should governments continue to use anti-gouging laws to correct supposed market failures occurring after natural disasters?