Assignment
Q1. In 1817, David Ricardo wrote the following, "England may be so circumstanced, that to produce the cloth may require the labour of 100 men for one year; and if she attempted to make the wine, it might require the labour of 120 men for the same time. To produce the wine in Portugal, might require only the labour of 80 men for one year, and to produce the cloth in the same country, might require the labour of 90 men for the same time."
a) In Ricardo's example, in the production of which good does Portugal have a comparative advantage?
b) In which country will the average wage, or standard of living, be higher?
Q2. Home has 1,200 units of labor available while Foreign has a labor force of 800. They can each produce two goods, apples and bananas. It takes 3 units of labor to produce one apple, and 2 units of labor to produce one banana in Home. Foreign's unit labor requirement in apple production is 5, while in banana production it is 1.
a) Graph each country's production possibility frontier.
b) In the absence of trade, what would be the price (opportunity cost) of apples in terms of bananas in each country?
c) Suppose the countries begin to trade. Describe the pattern of trade (which country will export or import which good). What might be the terms of trade (how many bananas will trade for one apple)?
d) Illustrate graphically that both Home and Foreign gain from trade.
Q3. According to data from the International Labor Organization, the average wage in the U.S. is roughly 8 times the average wage in Mexico. Suppose that we model the two countries as each able to produce just two goods, the two goods being beer and tequila. Suppose that a worker in the U.S. can produce a unit of tequila in 6 days or a unit of beer in 1 day. Suppose further that a worker in Mexico can produce the same unit of tequila in 36 days or the unit of beer in 10 days. Answer the following:
a) If Mexico has a labor force of 72 million, and the U.S. has a labor force of 120 million, construct the production possibilities frontier for each country.
b) Which country has the absolute advantage in each good? Which country has the comparative advantage in each good?
c) Calculate each country's opportunity cost of beer in terms of tequila.
d) Assume that each country completely specializes in the product in which it has a comparative advantage. Also assume that the free trade price of beer is $100/unit. Calculate the free trade price of tequila.
e) Which country gains the most from trade in this example?
Q4. Assume that home and foreign produce two goods, TVs and cars, according to the following:
|
In the no-trade equilibrium
|
|
Home
|
Foreign
|
|
TV
|
Cars
|
TV
|
Cars
|
|
WageTV = 12
|
WageC =
|
WageTV =
|
WageC = 6
|
|
MPLTV = 2
|
MPLC =
|
MPLTV =
|
MPLC = 1
|
|
PTV =
|
PC = 4
|
PTV = 3
|
PC =
|
Prices and Wages are measured in money terms (WageTV is the wage a worker earns in the TV industry), and MPL (marginal product of labor) can be thought of as the number of TVs (or Cars) that is made by the worker in one day. You'll notice that half the values are missing- your job is to fill them in.
If these two countries trade with one another, which country will export which good? Which country is the higher-wage country?
Q5. Australia is land abundant and India is labor abundant. Wheat is land intensive relative to textiles. Use a model of a two-factor economy and graphically demonstrate the pretrade and post-trade equilibria between these two countries. Which factors gain and which factors lose when trade arises between these two countries? Explain carefully.
Q6. Refer to the graph below to answer the following questions.
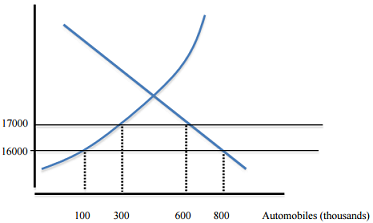
a) Suppose that the graph represents the market for automobiles in the home country. If the home country practices free trade and the world price of autos is $16,000 each, what quantity of autos are imported?
b) If the home country imposes a $1000/ auto tariff, what will be the approximate change in home country's producer's surplus? What will be the associated dead weight loss (you may calculate dollar values or simply refer to areas on the graph)?
c) Suppose the home country's government, instead of a tariff, decides to limit the number of auto imports to 300. How will the new outcome be different than under the tariff?
Q7. From the following figure, in which Dc and Sc refer, respectively, to the domestic demand and supply curves of cloth, and SF and SF+T refer, respectively, to the world supply curve of cloth under free trade and with a 50% import tariff imposed by the nation on the importation of cloth, determine:
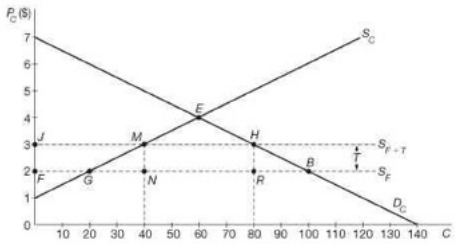
(a) the reduction in consumer surplus
(b) the increase in producer surplus or rent
(c) the tariff revenue
(d) the deadweight loss to the economy as a result of the tariff.