1 Random Numbers Generation
Later we are going to do simulations, and we need to be able to generate sequences of random numbers. Research how to do it on Excel/LibreO�ce and explain why these programs do not o�er good tools for this job. Also, if you have a smartphone, �nd an app that generates random numbers and tell me whether it is better or worse than Excel. Why? Hint: Google \pseudo random number".
Optional: Figure out how to generate random numbers on R and write a small code that generates 10 random numbers and prints them to the screen.
2 Current Events
Take a look at the World Economic Outlook 2012 (it is on blackboard) and write a summary about its description of the european situation. What do you think that is going to happen to the Euro zone?
3 Ricardian Model I
Suppose that there are only two countries and that they only make apples and bananas. The marginal productivities are such that 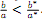 .
.
a) Explain the di�erence between absolute and comparative advantage.
b)Which country has a comparative advantage in apples? Which country has a comparative advantage in bananas?
c) In the free trade equilibrium, is it possible for the domestic country to ONLY make bananas and for the foreign country to ONLY make apples? Explain.
d) In the free trade equilibrium, is it possible for the domestic country to ONLY make apples and for the foreign country to ONLY make bananas? Explain.
e) Is it possible for both countries to produce the same good, i.e, both make apples, or both produce bananas? Why?
f) Now suppose that 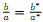 Redo parts a-e.
Redo parts a-e.
4 Ricardian Model II
Suppose that there are only two countries, domestic and foreign, and that they only make apples and bananas. The production functions are:
A = LA (1)
B = 5LB (2)
A = 2LA (3)
B = 14LB (4)
Labor supply is equal to 100 in each country, and there are no tari�s.
a) Derive the relative supply of apples in the world.
b) Suppose that the relative demand for apples in the world is:
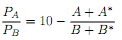
Compute the equilibrium. What is the equilibrium (relative) price of apples?
How many apples and bananas does each country make? Do they trade with each other?
c) Suppose that the demand for apples becomes:
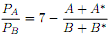
Redo part b). Compare your results. What happened to the price and quantities? What is the intuition?
d) Suppose that the demand becomes:
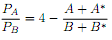
Redo part b). Do the countries trade with each other? Explain your answer.